Figure 6.
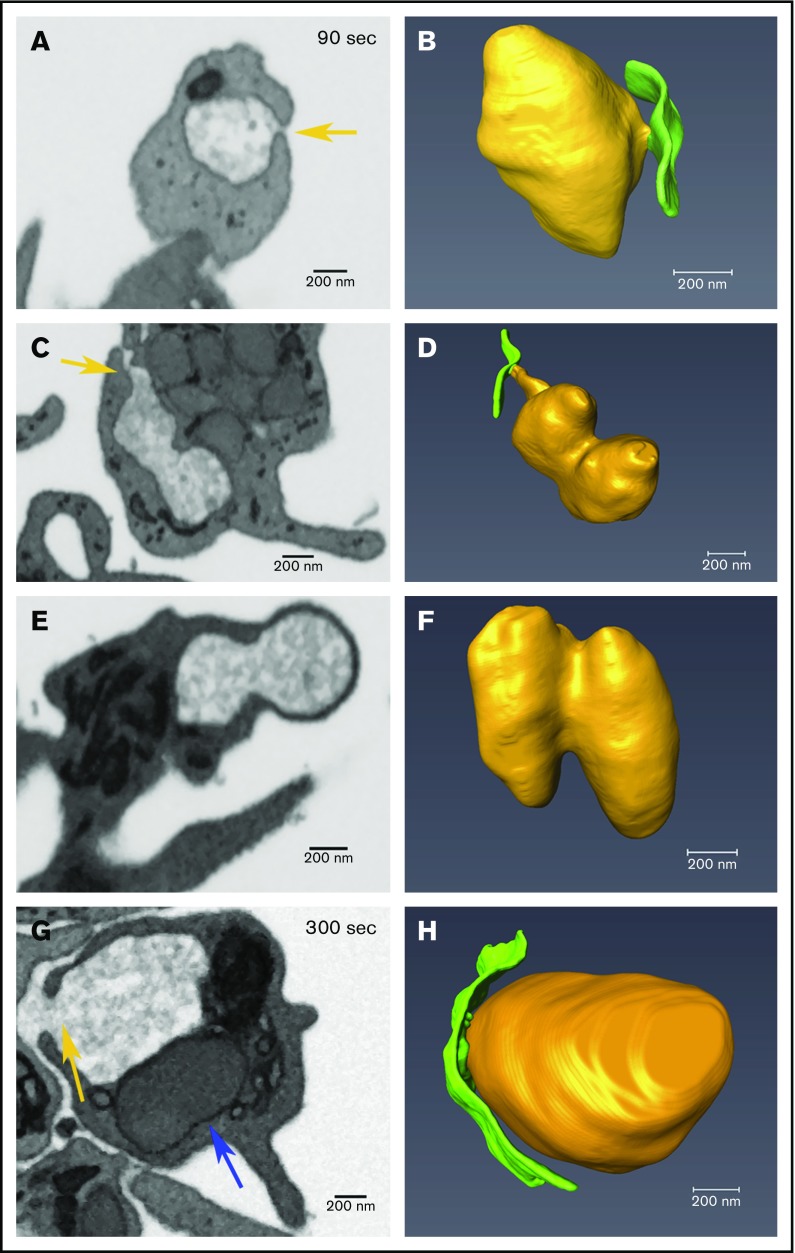
Decondensed α-granule membrane fusion in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Platelets were imaged by FIB-SEM at a nominal resolution of 5 nm in XYZ. Tan arrows point to examples of membrane fusion; 90 seconds stimulation (A-F) and 300 seconds stimulation (G-H). The left column shows single-slice images of platelets, and the right shows rendered images of decondensed granules (tan) and the PM (green). Two image sets show granules that track to the PM at 90 seconds stimulation, in one (A-B), the granule is linked to the PM fusion pore via a short neck, while in the other case the linkage to the fusion pore is by a longer pipe (C-D). (E-F) Two granules fused laterally (compound fusion), and these fail to track to either a PM or CS fusion pore complex. (G-H) A PM-granule fusion at 300 seconds with a larger neck/pipe. The blue arrow in panel G points to a rare condensed α-granule seen in a 300 seconds stimulated platelet. The incidence of α-granule fusion with PM and CS at various time points is quantified in Table 3. Bars represent 0.2 μm.