Fig. 10.
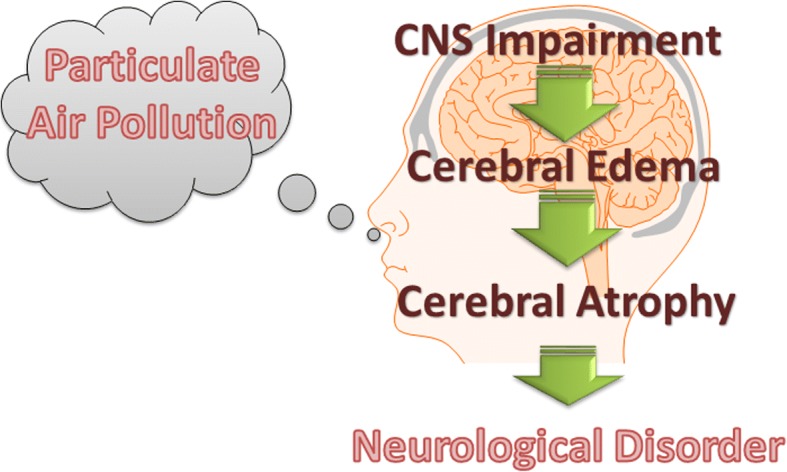
Illustration of the hypothetical pathways of particulate air pollution involved in the development of neurological disorders. Inhaled particulate air pollution is able to induce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, leading to central nervous system (CNS) impairment. The extracellular accumulation of fluid due to increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), results in formation of cerebral edema. The air pollution-induced edematous brain is repaired by protective mechanisms, leading to cerebral atrophy. Continuous exposure to particulate air pollution leads to the development of neurological disorders
