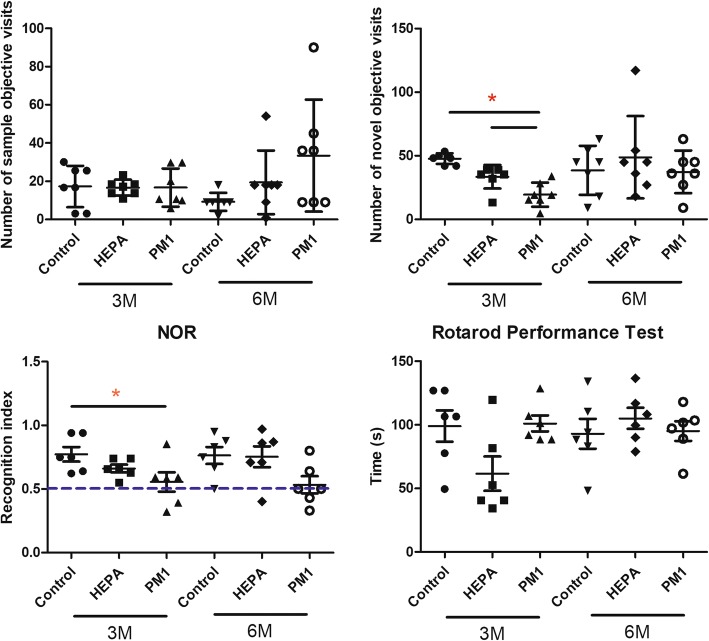
Fig. 4.
Behavioral observations in rats after 3 and 6 months of exposure to traffic-related air pollution. The novel object recognition (NOR) task and rotarod performance task (n = 6) were conducted in rats of the control, high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA), and particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of < 1 μm (PM1) groups. Three months of exposure to PM1 caused significant reductions in the number of novel object visits and recognition index compared to the control and HEPA groups. There were no differences in the rotarod performance test among the groups after exposure. * p < 0.05