Figure 2.
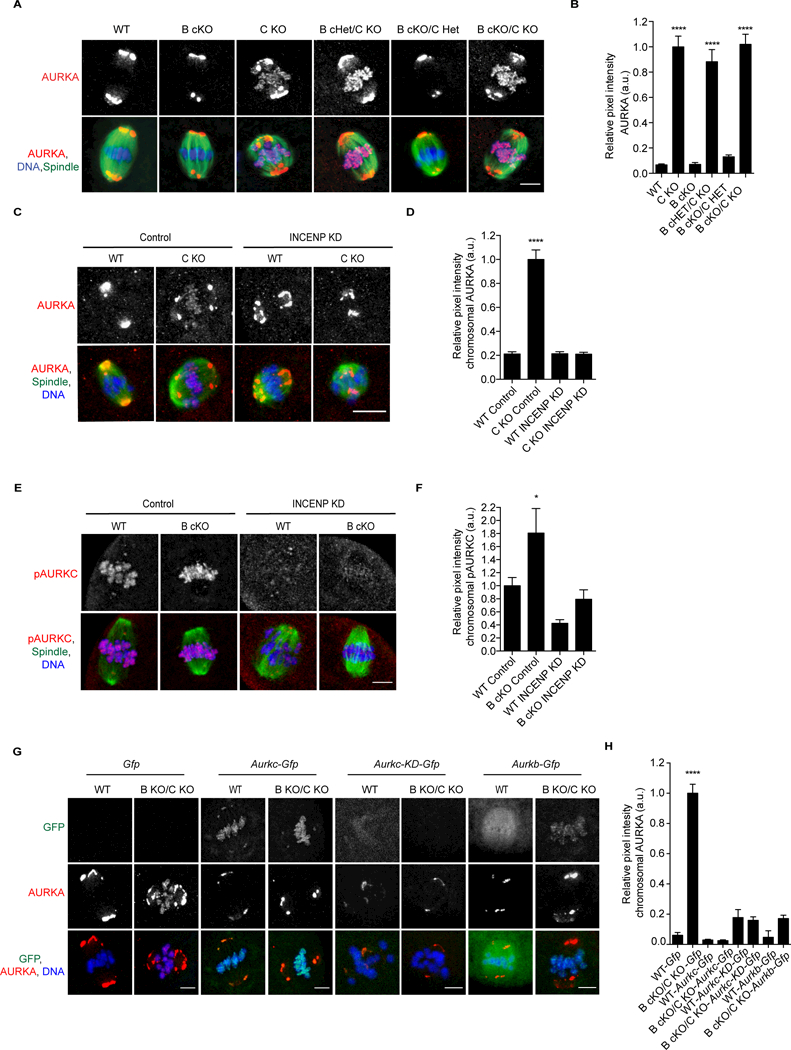
AURKC prevents AURKA from localizing to chromosomes.A) Prophase I (PI) oocytes from mice of the indicated genotypes were matured to metaphase of meiosis I (Met I) and stained to detect AURKA (red), spindle (a- tubulin, green), and DNA (DAPI, blue). Shown are representative confocal z- projections. Asterisks denote chromosome-localized AURKA. n = 1 animal/genotype/experiment; 4 experimental replicates B) Relative pixel intensity of chromosomal AURKA from A. Values normalized to B cKO/CKO. C-F) PI oocytes from the indicated genotypes were microinjected with morpholino oligonucleotides of either a scrambled sequence (control) or one designed to target INCENP (INCENP KD). Shown are representative z-projections of fixed oocytes that were matured to Met I. C) AURKA (red), spindle (a-tubulin, green), and DNA (DAPI, blue). D) Chromosome pixel intensity from C. n=4 animals/genotype/experiment; 2 experimental replicates. E) pAURKC (red), spindle (a-tubulin, green), and DNA (DAPI, blue). F) Pixel intensity of chromosomal AURKA from E. n=7 animals/genotype/experiment; 2 experimental replicates. G) WT or double KO PI oocytes were microinjected with the indicated cRNA. After ~15h, oocytes were matured to Met I and labeled to detect AURKA (red) and DNA (DAPI, blue). n = 3 animals/genotype/experiment, 3 independent experiments performed. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. * <0.05, ****p <0.0001, One-way ANOVA. Scale bars = 10 mm. See also Figures S1, S4.
