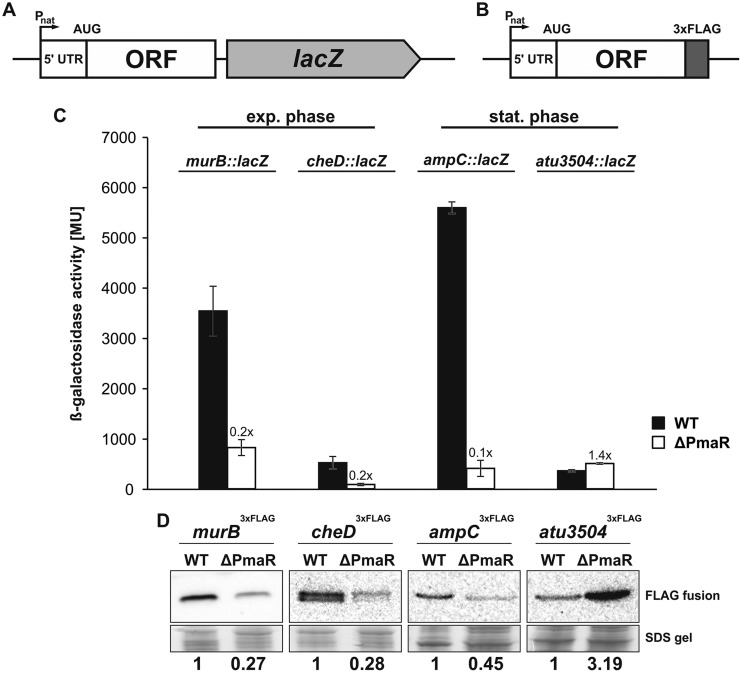
FIG 7.
Impact of PmaR on targets in vivo. Schematic drawing of transcriptional lacZ fusions (A) and translational fusions with 3×FLAG sequence (B). Reporter constructs were integrated into the chromosome of wild type and ΔPmaR mutant and expressed from the native promoter (Pnat). (C) Expression of targets in wild type (black bars) and ΔPmaR mutant (white bars) quantified by β-galactosidase activity (in Miller units) of transcriptional lacZ fusions. Mean standard deviation and induction rates relative to the wild type are indicated. Experiments were performed in triplicate, with three replicates each. (D) Western blot analysis of translational target fusions in wild type and ΔPmaR mutant via anti-3×FLAG M2 antibody. Quantification of detected signals was performed by pixel counting, and Coomassie-stained SDS-gels served as loading control. Experiments were performed in triplicate, with similar results. ORF, open reading frame.