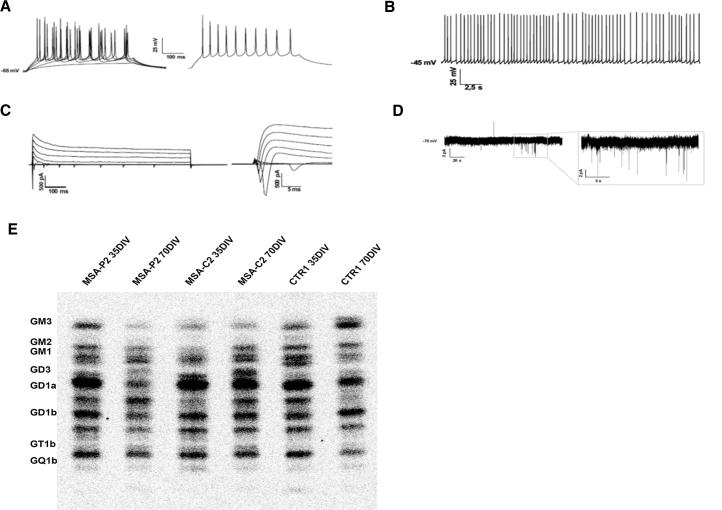
Figure 3.
Characterization of iPSC-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons: Second Part
(A) Current clamp recordings in whole-cell configuration of a representative neuron differentiated from MSA-P1 iPSCs at 56 DIV, showing evoked action potentials. On the right the maximal firing rate is shown, obtained injecting 260 pA of current.
(B) Spontaneous firing activity recorded in current clamp whole-cell configuration. Action potentials are fired at a frequency of 2–6 Hz.
(C) Representative traces of voltage-clamp recordings of inward and outward currents. Neurons were stimulated with voltage steps of 20 mV starting from 0 mV to 80 mV.
(D) Spontaneous post-synaptic potentials recorded in voltage-clamp whole-cell configuration from iPSC-derived neurons of MSAP2 at 70 DIV. Neurons were clamped at −70 mV and did not show spontaneous post-synaptic potentials, with the exception of few spikes of low amplitude.
(E) Sphingolipid composition of iPSC-derived neurons in aqueous phase. Digital autoradiography of HPTLC performed using the solvent system 0.2% chloroform/methanol/calcium chloride 50:42:11 (v/v/v).