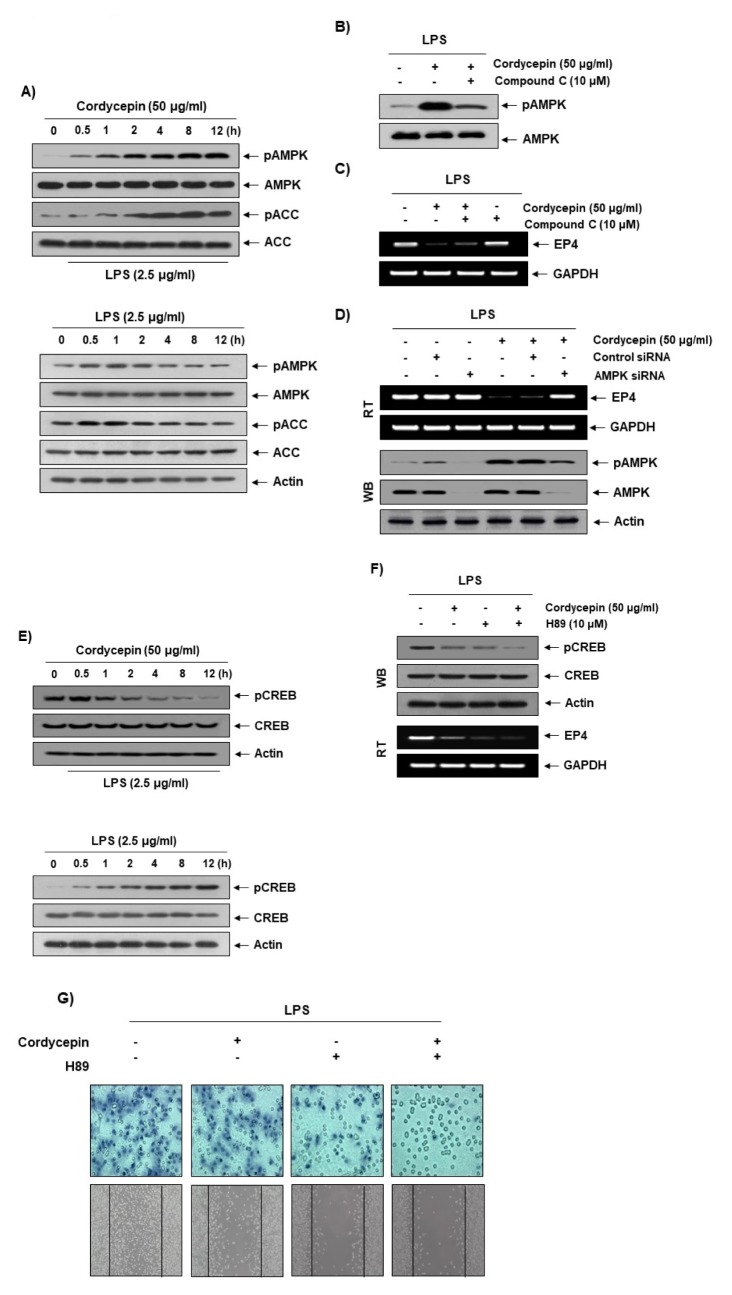
Fig. 4.
Involvement of the AMPK pathway in the reduction of EP4 expression by cordycepin. (A; upper panel) Cells were pretreated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for 1 h prior to treatment with cordycepin (50 μg/ml) for the indicated times. (A; lower panel) Cells were treated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Immunoblotting analyses were performed with anti-pAMPK, anti-AMPK, anti-pACC, and anti-ACC antibodies. (B) The effects of cordycepin and compound C on AMPK activation in LPS-stimulated HCT-116 cells. Cells were pretreated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for 1 h prior to treatment with either cordycepin (50 μg/ml) only or both cordycepin and compound C (10 μM) for 12 h. (C) The effects of cordycepin and compound C on EP4 expression in LPS-stimulated cells. Cells were pretreated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for 1 h prior to treatment with either cordycepin (50 μg/ml) only or both cordycepin and compound C (10 μM) for 12 h. (D) The cells were transfected with AMPK small interfering (siRNA) or control siRNA for 24 h. The transfected cells were treated with 50 μg/ml cordycepin for 48 h. (E; upper panel) Cells were pretreated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for 1 h prior to treatment with cordycepin (50 μg/ml) for the indicated times. (E; lower panel) Cells were treated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Cells were pretreated with LPS (2.5 μg/ml) for 1 h prior to treatment with either cordycepin (50 μg/ml) only or both cordycepin and H89 (10 μM) for 12 h. Then, we performed Western blot and RT-PCR (F) as well as cell migration and invasion assay (G).