Fig. 3. KCNEs alter MTX effects on KCNQ1.
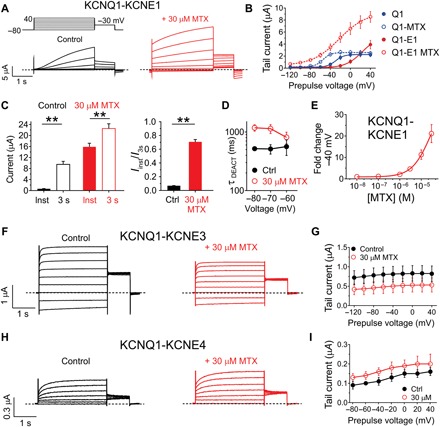
All error bars indicate SEM. (A) Averaged KCNQ1-KCNE1 current traces in response to voltage protocol (upper left inset) in the absence (control) or presence of 30 μM MTX (n = 5). Dashed line indicates zero current level in this and all following current traces. (B) Mean effects of 30 μM MTX on KCNQ1 and KCNQ1-KCNE1 raw tail currents at −30 mV after prepulses as indicated [as in (A); n = 5]. (C) Mean instantaneous (inst) current compared to current after 3 s (both at +40 mV) for KCNQ1-KCNE1 channels in the absence (control) versus presence of MTX (30 μM). **P < 0.01 (n = 5). Left: Raw currents. Right: Instantaneous current/3-s current. (D) Mean KCNQ1-KCNE1 channel deactivation rate versus voltage in the absence (control) and presence of MTX (30 μM). (E) Mean dose response for effects of MTX on KCNQ1-KCNE1 current magnitude at −40 mV (n = 5). (F) Averaged KCNQ1-KCNE3 current traces in response to voltage protocol [as in (A)] in the absence (control) or presence of 30 μM MTX (n = 8). (G) Mean effects of 30 μM MTX on KCNQ1 and KCNQ1-KCNE3 raw tail currents at −30 mV after prepulses as indicated [as in (F); n = 8]. (H) Averaged KCNQ1-KCNE4 current traces in response to voltage protocol [as in (A)] in the absence (control) or presence of 30 μM MTX (n = 5). (I) Mean effects of 30 μM MTX on KCNQ1 and KCNQ1-KCNE4 raw tail currents at −30 mV after prepulses as indicated [as in (H); n = 5).
