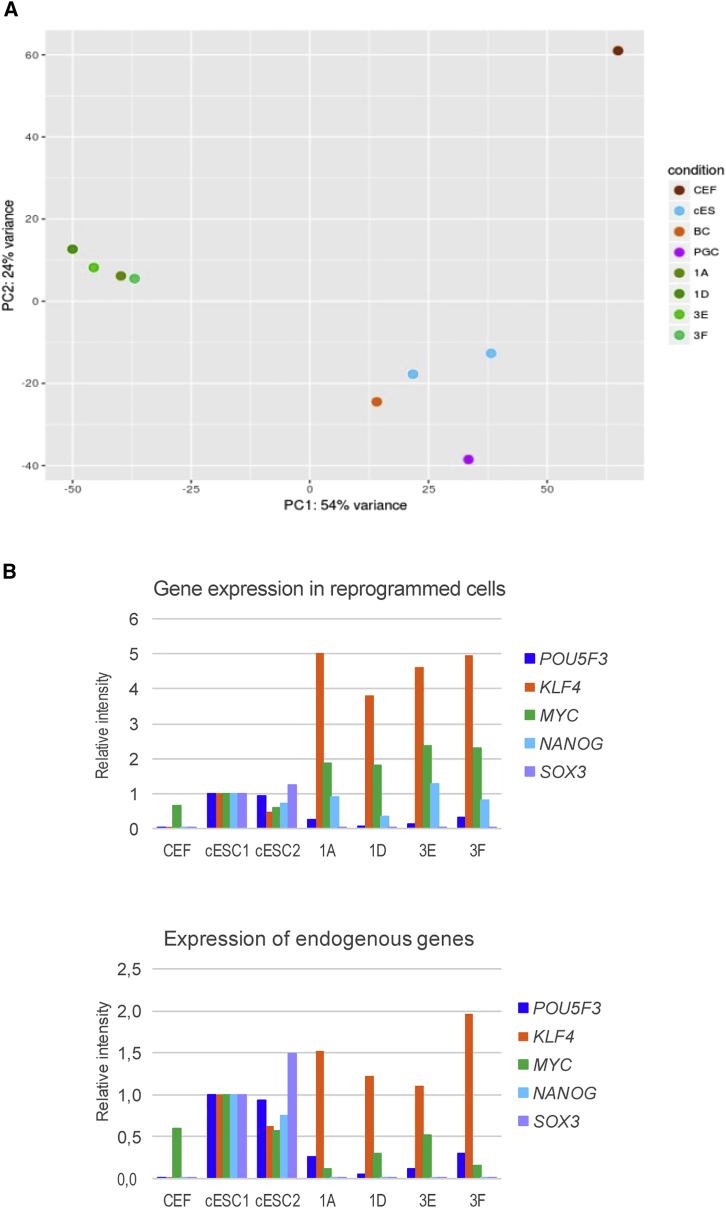
Figure 6.
Molecular Features of the Reprogrammed Clones
(A) Principal-component analysis revealed that the reprogrammed clones (1) were different at the molecular level from the starting CEFs, (2) clustered together leading to a common cell type generated by the reprogramming process, and (3) differed from spontaneously established cESCs (two independent isolates, cESC-1 and cESC-2, derived from BCs). Primordial germ cells clustered with the previous cell types (cESCs and BCs) and helped define the chicken pluripotent stem cell molecular signature.
(B) The expression profile of exogenous and endogenous reprogramming genes reveals the expression of endogenous POU5F3, KLF4, and c-MYC, but an absence of NANOG endogenous expression as also detected by the deep sequencing analysis.