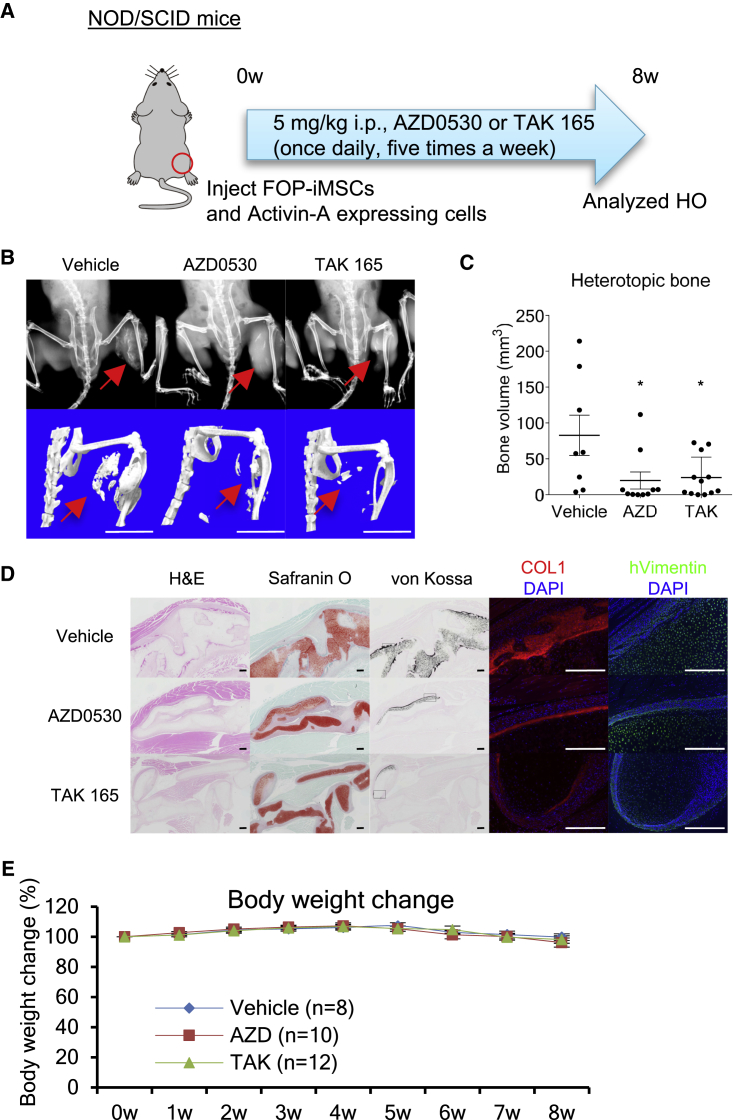
Figure 6.
AZD0530 and TAK 165 Suppressed HO Derived from FOP-iMSCs In Vivo
(A) Schematic of the in vivo efficacy study utilized a human FOP-iPSC-based in vivo model. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of 5 mg/kg AZD0530 or TAK 165 (once daily, five times a week) suppressed the HO derived from FOP-iMSCs triggered by activin A. Eight weeks after transplantation and drug administration, mice were analyzed.
(B) X-ray (upper panels) and μCT (lower panels) observations. Scale bars, 10 mm.
(C) Average heterotopic bone volume.
(D) Histological analysis of the cell-transplanted region. H&E, safranin O, von Kossa, anti-COL1, and anti-human vimentin staining are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm (H&E, safranin O, and von Kossa) and 500 μm (COL1 and hVimentin).
(E) Body weight change (%) of mice administered compounds.
Results are the mean ± SE, n = 8 (vehicle), n = 10 (AZD0530), or n = 12 (TAK165). ∗p < 0.05 by Dunnett's multiple comparisons t test compared with vehicle treatment group (C). No significant differences between the AZD- or TAK-administered group compared with the vehicle group in two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons t test (E).