Fig. 2.
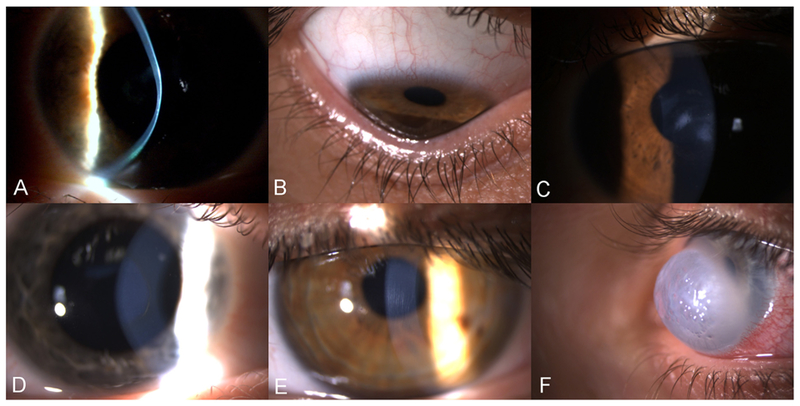
Slit lamp images of KC signs. A: Corneal thinning at the apex of the cone. B: Corneal ectasia, with indentation of the inferior eyelid upon down gazing C: Paracentral stromal scars. D: Fleischer’s ring, a pigmented, often incomplete line of iron deposits running around the base of the cone. E: Vogt’s stria: fine vertical lines, which are breaks in the deep stroma and Descemet’s membrane. F: Corneal hydrops, the most acute presentation of KC. Diffuse stromal opacity and edema, caused by breaks in the Descemet’s membrane leading to influx of fluid in the stroma.
