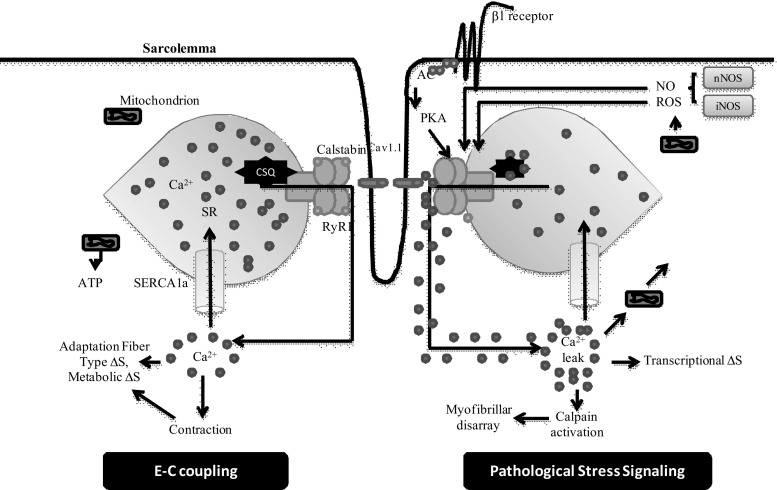
Fig. 2.
Stress responses in skeletal muscle during E-C coupling. Depolarization of the T-tubule membrane activates Cav1.1, triggering SR Ca2+ release through RyR1 and leading to sarcomere contraction, a process known as E-C coupling. During pathological stress intracellular signaling pathways activated and affect RyR1 function and alter E-C coupling. Stress-induced RyR1 dysfunction can result in SR Ca2+ leak, which potentially activates numerous Ca2+-dependent cellular damage mechanisms. AC, adenylate cyclise; CSQ, Calsequestrin; SERCA1a, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium-ATPase; RyR1, Ryanodine receptor 1