Figure 5. Suggested effects of PLC, FLU, NIC and the combination of NIC and FLU on intracellular calcium concentration and tDCS‐induced LTP‐like plasticity.
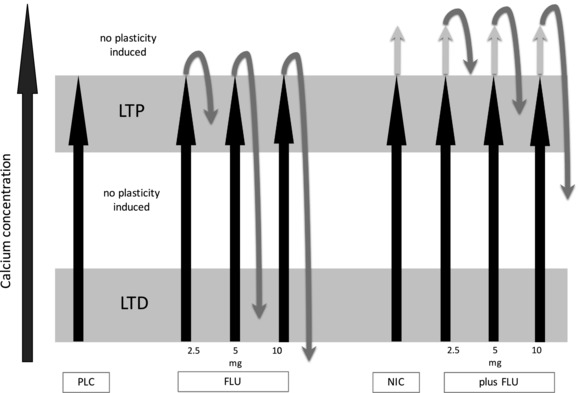
Assumed association between the changes of intracellular calcium concentration (x‐axis) and induction of tDCS‐induced excitability changes. Gradual enhancement of calcium concentration can either induce LTD, LTP or no plasticity. The combination of tDCS and PLC leads to LTP (black arrow alone). Additional administration of FLU in increasing doses gradually lowers intracellular calcium levels to either weaker LTP‐, LTD‐ or no plasticity induction (black and grey arrows). The combination of tDCS and NIC leads to a calcium overflow that prevents LTP induction (black and grey arrow). Gradually decreasing calcium concentration with additional administration of FLU re‐establishes tDCS‐induced LTP‐like plasticity in medium dosages (black and grey arrows).
