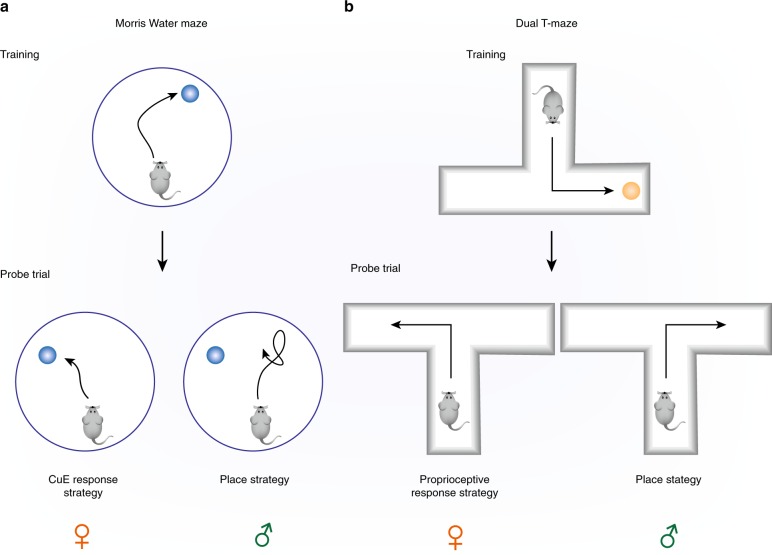
Fig. 3.
Schematic illustrations for sex differences in spatial learning strategies in the (a) Morris Water Maze and (b) Dual T-Maze Task. Males are more likely to use geometric cues (place strategy) and females are more likely to use landmark cues (cue response strategy) or proprioceptive cues (proprioceptive response strategy) to reach a destination [135, 140–143]