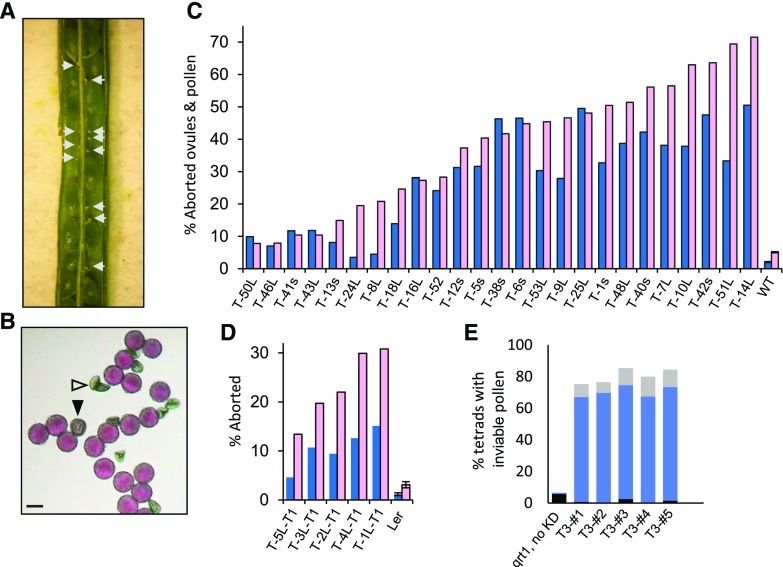
Figure 4.
Aborted ovules and pollen resulting from PIRL6 knockdown. PIRL6 inverted repeat constructs were introduced into wild-type WS Arabidopsis by A. tumefaciens-mediated transformation; transgenic T1 plants harboring the RNAi construct were identified by glufosinate resistance and confirmed by genomic PCR. T1 plants were hemizygous and were scored directly for segregating ovule and pollen defects. A, A silique from a T1 plant (T-48L-T1) containing seeds from successfully fertilized ovules segregating with aborted ovules (white arrows). B, Alexander-stained pollen produced by T1 plant T-48L-T1, showing the segregation of aborted (white triangle) and stunted (black triangle) grains. Bar = 20 µm. C, Percentages of abnormal or aborted pollen (blue) and aborted ovules (pink) in 25 T1 plants independently transformed with PIRL6 RNAi constructs and in wild-type controls (WT). The ranges of n values are as follows: pollen, 61 to 1,468; ovules, 105 to 191. L or s in plant line labels indicates the PIRL6-RNAi construct introduced in that line (see text). D, Replication of the RNAi-induced phenotype in the Ler ecotype. Percentages are shown for abnormal or aborted pollen (blue) and aborted ovules (pink) in five Ler T1 plants independently transformed with the PIRL6-RNAi(L) construct. The n value ranges are as follows: pollen, 352 to 1,124; ovules, 142 to 178. In C and D, means and se are shown only for untransformed controls; se was not determined for T1 samples because values were obtained, by definition, from individual transformed plants. E, Gametophytic basis of PIRL6-KD pollen defects, shown by meiotic segregation in pollen tetrads produced by five individual PIRL6-KD hemizygotes in a qrt1 background. Black bars, percentage of tetrads with one dead pollen grain; solid blue bars, percentage of tetrads with two dead pollen grains; light gray bars, percentage of tetrads with more than two dead pollen grains (the range of n values is as follows: 89–198 tetrads per plant).