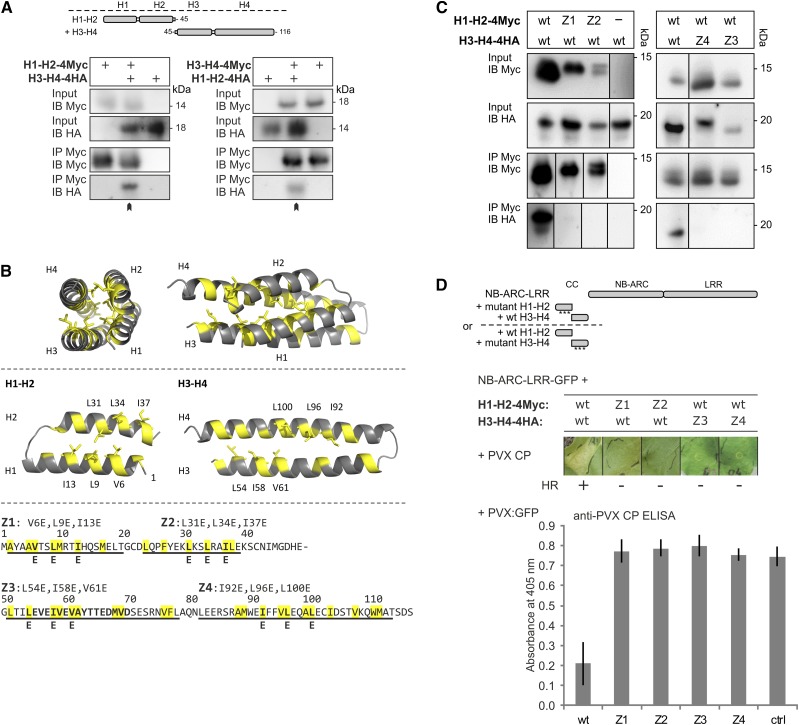
Figure 1.
Assessing the role of the hydrophobic interface between the N- and C-terminal two-helix segments of the Rx1 CC domain. A, The two halves of the Rx1 CC interact in a coimmunoprecipitation assay. Combinations of coexpressed CC fragments H1-H2 (amino acids 1–45) and H3-H4 (amino acids 45–116) fused to 4xMyc or 4xHA affinity tags were subjected to anti-c-Myc immunoprecipitation. Extracts of leaves expressing the single strands were included as controls for aspecific binding and protein stability. The blots show the cell extract used as input and the result of the immunoprecipitation as detected with anti-c-Myc and anti-hemagglutinin (HA) antibodies. B, Targeted mutagenesis of hydrophobic residues in the heptad repeats. A set of constructs was made in which three apolar residues per α-helix were exchanged for Glu (E). The groups of three substitutions were named Z1 to Z4 in correspondence with the predicted helix in which they are positioned. Hydrophobic positions of the heptad repeat are indicated in yellow in the CC structure and the amino acid sequence. The substituted residues are indicated. C, Effects of mutations Z1 to Z4 on the intramolecular interaction of the Rx1 CC domain. Mutant versions of H1-H2-4Myc were coexpressed with wild-type (wt) H3-H4-4HA or vice versa. The H1-H2-4Myc constructs were pulled down by anti-Myc antibodies, and the coimmunoprecipitated H3-H4-4HA constructs were visualized by anti-HA immunoblot. Some of the lanes have been rearranged to align input and corresponding immunoprecipitation results; this is indicated by solid lines on the immunoblot. D, Mutant versions of H1-H2-4Myc and H3-H4-4HA were transiently expressed with Rx1 NB-ARC-LRR-GFP (amino acids 142–937) in the presence of the coat protein (CP106) of PVX to assess the cell death response. The combinations of the Rx1 segments are indicated in a schematic drawing. Images were taken 5 d post infiltration (dpi). To assess PVX resistance, variants of H1-H2 and H3-H4 were coinfiltrated in N. benthamiana leaves with the NB-ARC-LRR-GFP and a PVX:GFP amplicon. Virus accumulation was determined by anti-PVX CP ELISA of leaf extracts at 5 dpi with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated antibodies. p-Nitrophenol accumulation was detected via its A405. As a control (ctrl), PVX:GFP was expressed in the absence of Rx1.