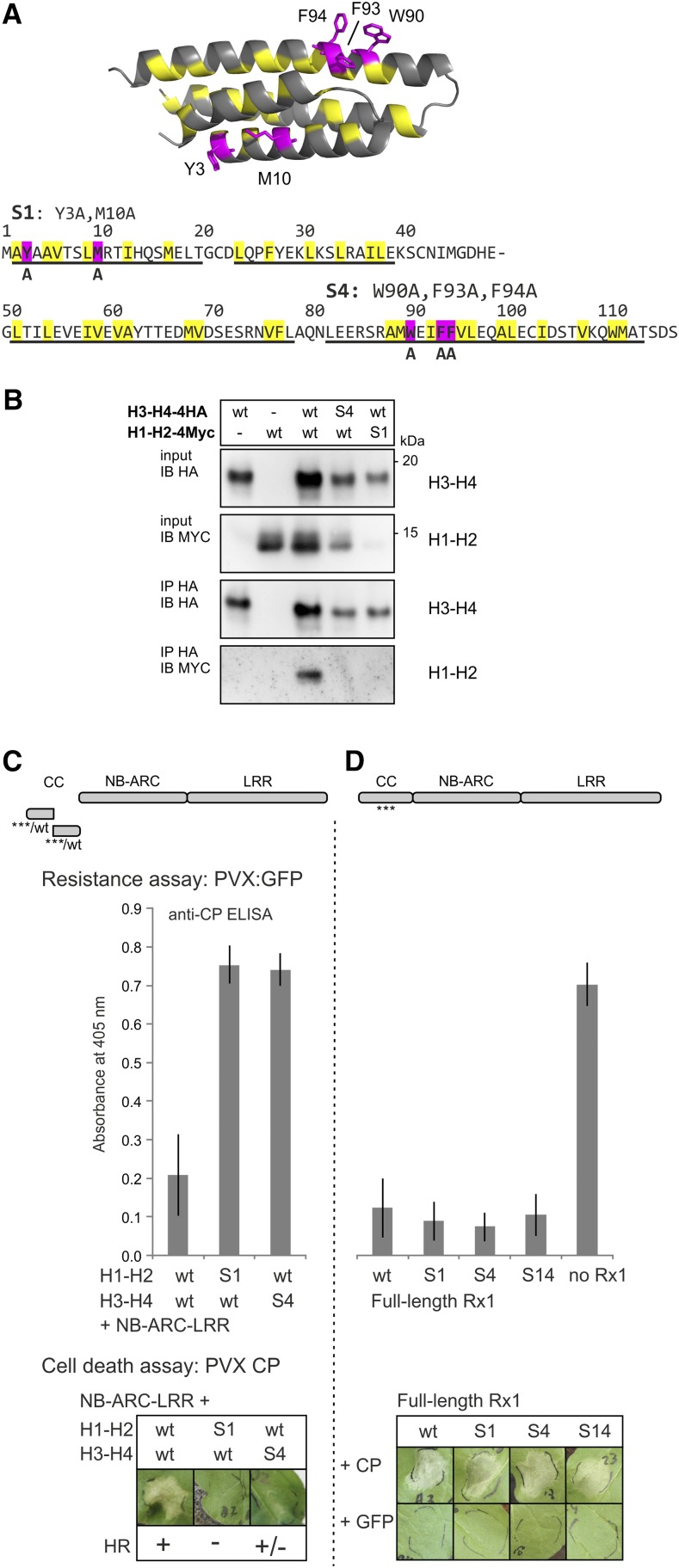
Figure 3.
Ala substitution of aromatic and hydrophobic surface residues in helix 1 and helix 4 of the CC. A, Two groups of mainly aromatic residues in the CC (highlighted in magenta in the structure and amino acid sequence) were substituted for Ala (A). In helix 1, Y3A and M10A were combined and named S1. In helix 4, the substitutions W90A, F93A, and F94A were introduced, and this combination was referred to as S4. Both groups of substitutions were introduced in several constructs, including the H1-H2 and H3-H4 CC strands and full-length Rx1. B, Effects of the S1 and S4 mutations on the interaction between the H1-H2 and H3-H4 strands of the CC. Anti-HA immunoprecipitation was performed to study the interaction between coexpressed wild-type (wt) and mutated (S1 and S4) versions of the H1-H2-4Myc and H3-H4-4HA constructs. Expression of only H1-H2-4Myc or H3-H4-4HA was used as a negative control. C, The effects of the S1 and S4 mutations on Rx1 functioning were tested for the transcomplementation of H1-H2 and H3-H4 with the NB-ARC-LRR, as shown by a schematic drawing. Resistance was tested by coexpressing the Rx1 constructs with the PVX:GFP amplicon in N. benthamiana followed by an anti-PVX CP ELISA with extracts of the infiltrated leaf material. Error bars indicate the sd of six samples. The ability of the constructs to induce cell death (HR) was assessed by coexpression of the complementary Rx1 fragments with the avirulent PVX elicitor CP106. D, The effects of S1 and S4 on the functioning of full-length Rx1 were tested in transient PVX resistance and cell death assays. Mutant constructs (S1, S4, or the combination S14) and wild-type Rx1 were coexpressed with a PVX:GFP amplicon to test for resistance. A leaf infiltrated with PVX:GFP, but not Rx1, was included as a control. Error bars indicate the sd (n = 6). To assess the ability of the mutants to induce a cell death response, the full-length Rx1 constructs were coexpressed with the avirulent PVX CP, and images of the response were taken at 3 dpi. As a control for the autoactive cell death response, the Rx1 constructs were coexpressed with GFP.