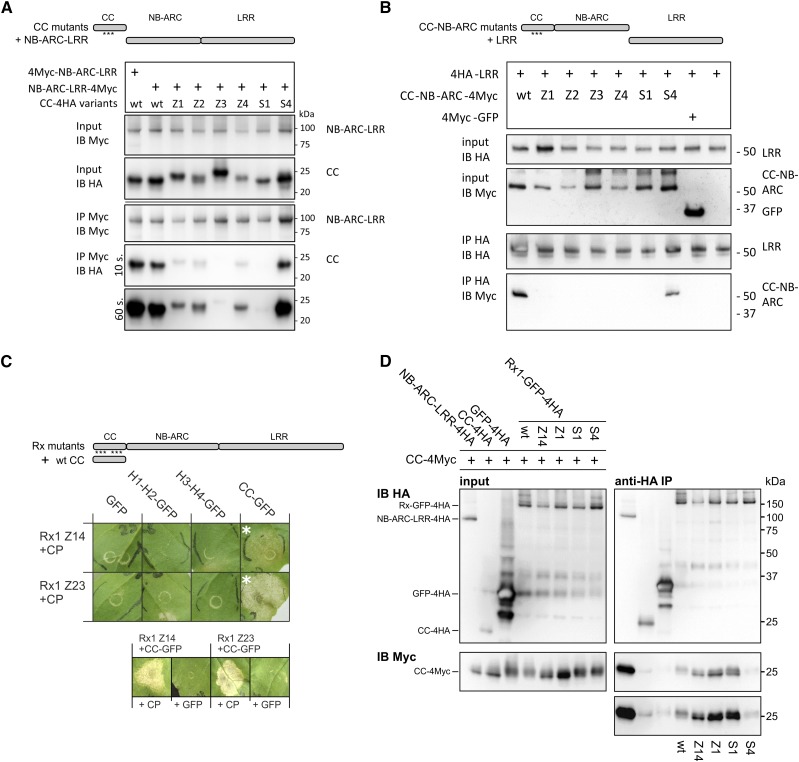
Figure 5.
Effects of the mutations in the CC on the domain interactions of Rx1. A, Effects of the mutations Z1 to Z4, S1, and S4 on the interaction between the CC and the NB-ARC-LRR of Rx1. A Myc-tagged construct of the Rx1 NB-ARC-LRR (amino acids 144–937) was coexpressed with 4xHA-tagged constructs of the wild-type (wt) and mutant CC. The NB-ARC-LRR was pulled down using anti-Myc antibodies, and the coimmunoprecipitation of the CC constructs was detected via an anti-HA immunoblot. B, Immunoprecipitation assay testing the effect of the CC mutations on the interaction between the CC-NB-ARC and LRR of Rx1. 4Myc-tagged CC-NB-ARC constructs were coexpressed with 4HA-LRR. Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-Myc antibodies, and the coprecipitation of the HA-tagged LRR was visualized by anti-HA immunoblot. C, Complementation of functionality for full-length Rx1 mutants by coexpression of the wild-type CC. The full-length Rx1 constructs carrying the combined Z14 or Z23 mutations were coexpressed with wild-type versions of the individual CC strands (H1-H2 and H3-H4) or the complete CC (shown in the schematic drawing at top). The PVX CP was coexpressed to test if the presence of the CC or CC strands could restore the ability of the Rx1 mutant to initiate a cell death response. The combinations in which a cell death occurred are marked with white asterisks. These combinations were tested with GFP instead of the CP to test for autoactivity (row of images at bottom). D, Interaction study to test if mutations in the CC disrupt the interaction between the CC and NB-ARC-LRR in the full-length Rx1 protein and, thereby, make the CC-binding surface on the NB-ARC-LRR accessible for coexpressed CC constructs. GFP-4HA-tagged constructs of full-length Rx1 (wild type, Z14, Z1, S1, and S4) were coexpressed with a wild-type CC-4Myc construct. The full-length Rx1 constructs were immunoprecipitated by anti-HA antibodies, and the coimmunoprecipitation of the CC was detected via anti-Myc immunoblot. The truncated NB-ARC-LRR served as a positive control for this interaction. HA-tagged CC and HA-tagged GFP constructs were used as negative controls.