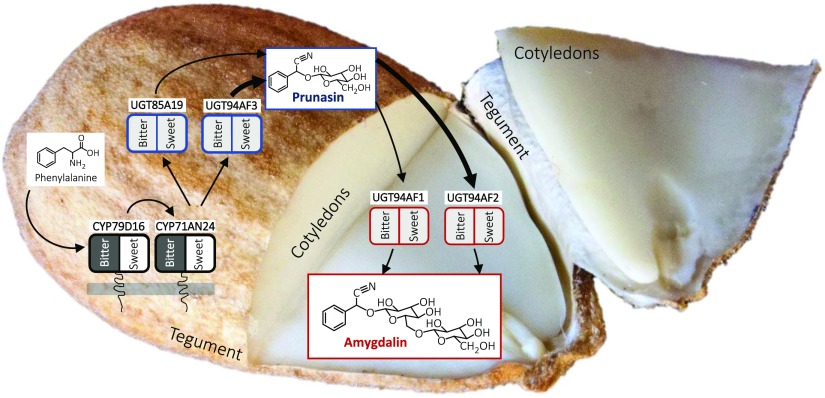
Figure 6.
The amygdalin biosynthetic pathway and its compartmentalization in almond. In the tegument, Phe is transformed into prunasin by the action of two P450s and UGTs. The expression levels of the two P450s PdCYP79D16 and PdCYP71AN24 are different between sweet (white background, no expression) and bitter (black background, very high expression). The expression of the UGT-encoding genes is not significantly different in the sweet and bitter phenotypes. Following transport to the cotyledons, prunasin is converted into amygdalin by the action of diglucosyltransferases encoded by PdUGT94AF1 or PdUGT94AF2. These two genes also are not differentially expressed in the cotyledons. The expression levels of PdUGT94AF3 and PdUGT94AF2 are higher than those of PdUGT85A19 and PdUGT94AF1, respectively (Supplemental Fig. S5), which is represented by thicker arrows. Thus, the sweet kernel trait reflects the lack of expression of PdCYP79D16 and PdCYP71AN24.