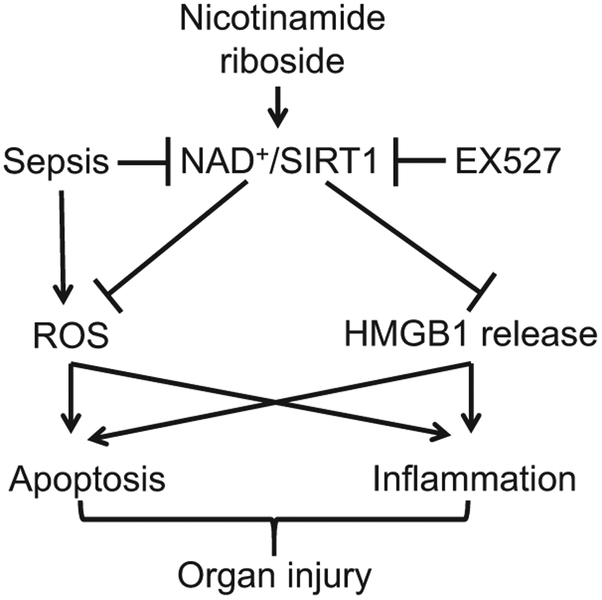
Fig. 9.
Schematic of nicotinamide riboside/NAD/SIRT1 pathway in sepsis. Sepsis induces ROS production and inhibits NAD+/SIRT1 signaling, leading to HMGB1 release, apoptosis and inflammation, which contribute to organ injury. Nicotinamide riboside is converted to NAD+ and subsequently activates SIRT1 signaling. Activation of SIRT1 inhibits ROS production and HMGB1 release thereby attenuating apoptosis and inflammation, and finally protecting against organ injury in sepsis. EX527 inhibits SIRT1 activation and reverses the protective effects of nicotinamide riboside on septic organ injury.