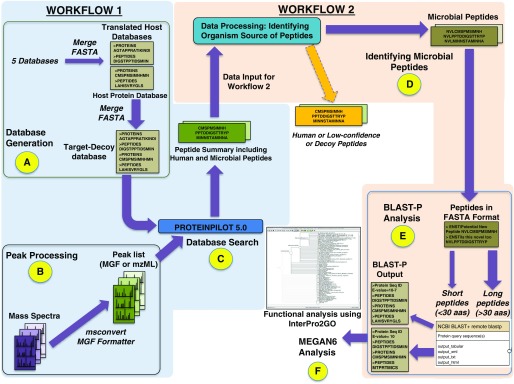
Figure 1.
Metaproteomics workflow in Galaxy-P to identify bacterial peptides in BAL fluid. In the first workflow (steps A–C), a database was generated (A) and peak processing RAW files were converted to mzml and MGF files and searched with ProteinPilot version 5.0.0, 1654 revision: 1656. (B). The outputs from these steps were used for a database search (C) to generate a list of both human and bacterial peptide-spectrum matches (PSMs) (Table E1). In the second workflow (steps D–F), bacterial PSMs were parsed out by eliminating human-origin peptides from the list (D). The microbial peptides were subjected to BLAST-P analysis (E) against the NCBInr database to generate an output for subsequent MEGAN6 analysis. MEGAN software uses a bitscore threshold to assign matches. Any match that has a bitscore below the threshold is not used to assign taxonomy. If all matches for a taxonomy or function are below the threshold, it is marked as unassigned. Peptides that do not have a match because of an absence of sequences in the InterPro2GO mapping file are termed “No Hits” (F).