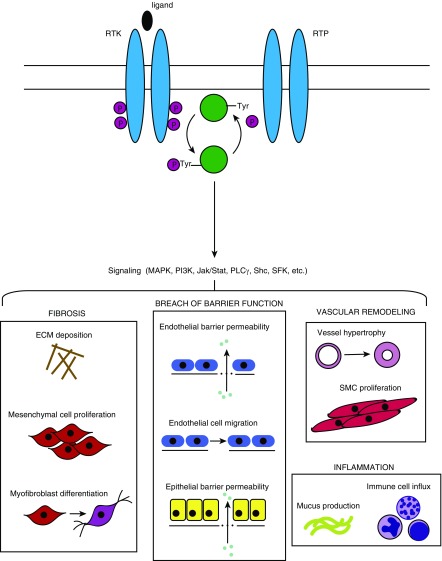
Figure 1.
Basic protein tyrosine kinase and protein tyrosine phosphatase activity and consequences for pulmonary pathology. RTKs and PTKs, located on the cell surface, bind ligands on their extracellular domain, which induces dimerization and phosphorylation of the intracellular catalytic domain. The active enzyme either phosphorylates or dephosphorylates the substrate (in the case of kinases or phosphatases, respectively). Subsequent downstream signaling can involve multiple signaling cascades and pathways, resulting in diverse physiologic consequences that are relevant to the pathogenesis of various pulmonary disease states. ECM = extracellular matrix; Jak/Stat = Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription; MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase; P = phosphate; PLCγ = phospholipase Cγ; RTK = receptor tyrosine kinase; RTP = receptor tyrosine phosphatase; Tyr = tyrosine; SFK = Src family kinase; Shc = Src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein 2; SMC = smooth muscle cell.