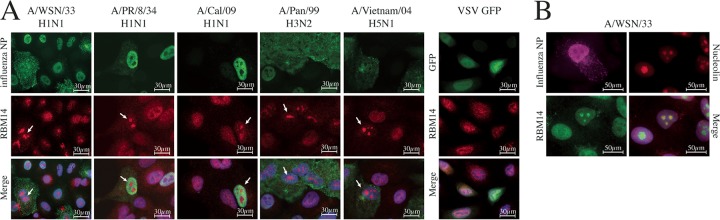
FIG 5.
RBM14 relocalizes to the nucleolus in IAV-infected cells. (A) Wide-field immunofluorescence microscopy images show that RBM14 relocalizes to a distinct subnuclear compartment in IAV-infected cells. A549 cells were infected with the indicated influenza A viruses at an MOI of 1.0 and were fixed 6 h postinfection. The cells were stained with anti-RBM14 antibody (red), anti-IAV NP antibody (green), and DAPI nuclear stain (blue). RBM14 relocalization (indicated by white arrows) was observed with a range of influenza A virus subtypes but not with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV; far right panel). Magnification, ×63. Scale bars are indicated on the figure. (B) WSN-infected A549 cells were stained with anti-nucleolin antibody (red), and it was observed that this staining coincided with anti-RBM14 staining (green) in infected cells (stained with anti-IAV NP antibody; magenta), indicating that IAV drives RBM14 to the nucleolus in infected cells. Magnification, ×63. Scale bars are indicated on the figure.