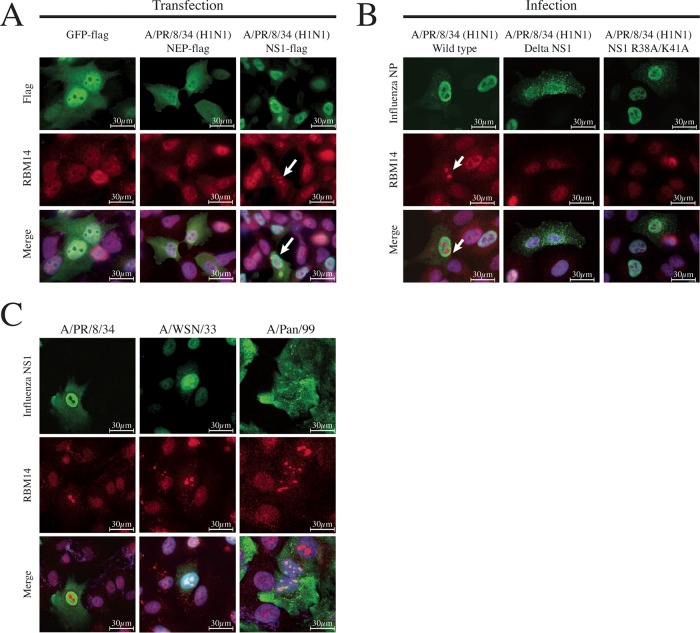
FIG 6.
NS1 is necessary and sufficient for RBM14 nucleolar relocalization. (A) Individual Flag-tagged IAV expression plasmids were transfected into A549 cells and subsequently fixed and stained with anti-Flag antibody (green), anti-RBM14 antibody (red), and DAPI 24 h posttransfection. GFP-Flag and NEP-Flag (a representative IAV protein) did not elicit RBM14 relocalization (left and middle panels), while NS1-Flag did exhibit this relocalization phenotype (indicated by white arrow). Magnification, ×63. Scale bars are indicated on the figure. (B) A549 cells were infected with wild-type influenza A/PR/8 (H1N1) virus (left panel), influenza A/PR/8 (H1N1) ΔNS1 virus (middle panel), and recombinant PR/8 dsRNA binding NS1 mutant R38A/K41A (right panel), and cells were fixed 6 h postinfection. Cells were stained with anti-IAV NP antibody (green), anti-RBM14 antibody (red), and DAPI. By wide-field microscopy, RBM14 was observed to relocalize upon infection with wild-type virus (white arrow) but not with ΔNS1 virus or the dsRNA binding mutant NS1 virus. Magnification, ×63. Scale bars are indicated on the figure. (C) A549 cells were infected with three influenza A viruses: A/PR/8 (H1N1), A/WSN/33 (H1N1), and A/Pan/99 (H3N2). The cells were fixed 6 h postinfection and stained with anti-NS1 (green), anti-RBM14 (red), and DAPI. Wide-field microscopy shows that PR/8 NS1 (left panel) did not localize to the nucleolus at 6 h; however, the NS1 proteins from WSN and Pan/99 (middle and right panels) exhibited mild and strong nucleolar localization, respectively. Magnification, ×63. Scale bars are indicated on the figure.