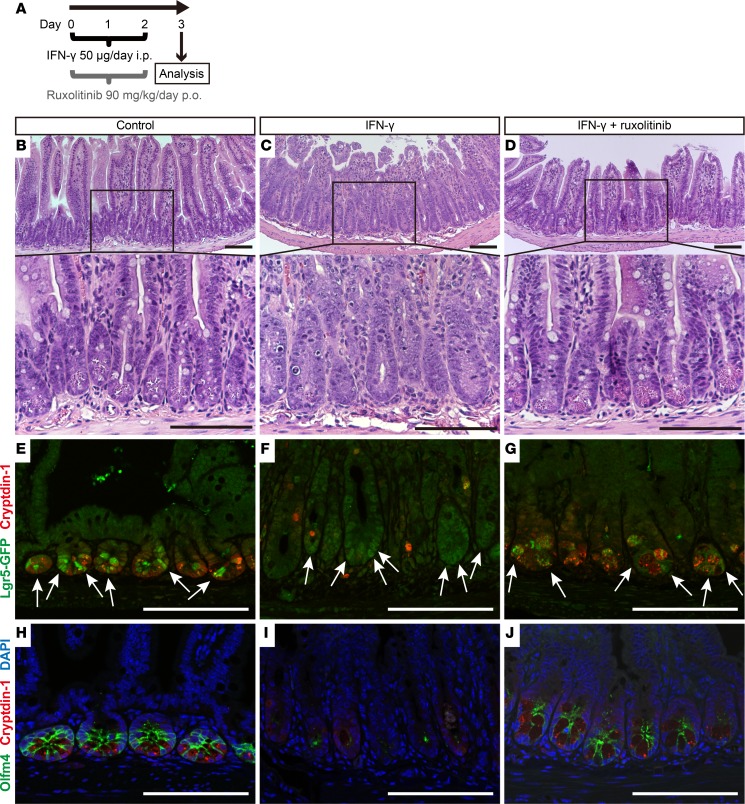
Figure 8. Exogenous IFN-γ depletes Paneth cells and modifies the expression of rapidly cycling ISC markers in vivo.
(A) Overall experimental scheme for IFN-γ and ruxolitinib administration in mice. Ileum samples were collected 72 hours after the first dose of IFN-γ. Histochemical staining (H&E) of ileum sections from control (B), IFN-γ–treated (C), or IFN-γ + ruxolitinib–treated (D) C57BL/6 mice. (E–J) Confocal image for cryptdin-1 (red) of Lgr5-EGFP-ires-creERT2 mouse ileum sections. (E–G) Lgr5-GFP+ ISCs are green (white arrows). (H–J) Sections stained for Olfm4 (green) with DAPI (blue). Control (E and H), IFN-γ–treated (F and I), and IFN-γ + ruxolitinib–treated (G and J) ileum sections are shown. The results are representative of 2 experiments. Note that some ileal crypts of IFN-γ–treated mice lack Paneth cells and Olfm4+ ISCs (I), but crypts that are faintly positive for Lgr5-GFP cells are still evident (F). Scale bars: 100 μm.