Figure 1.
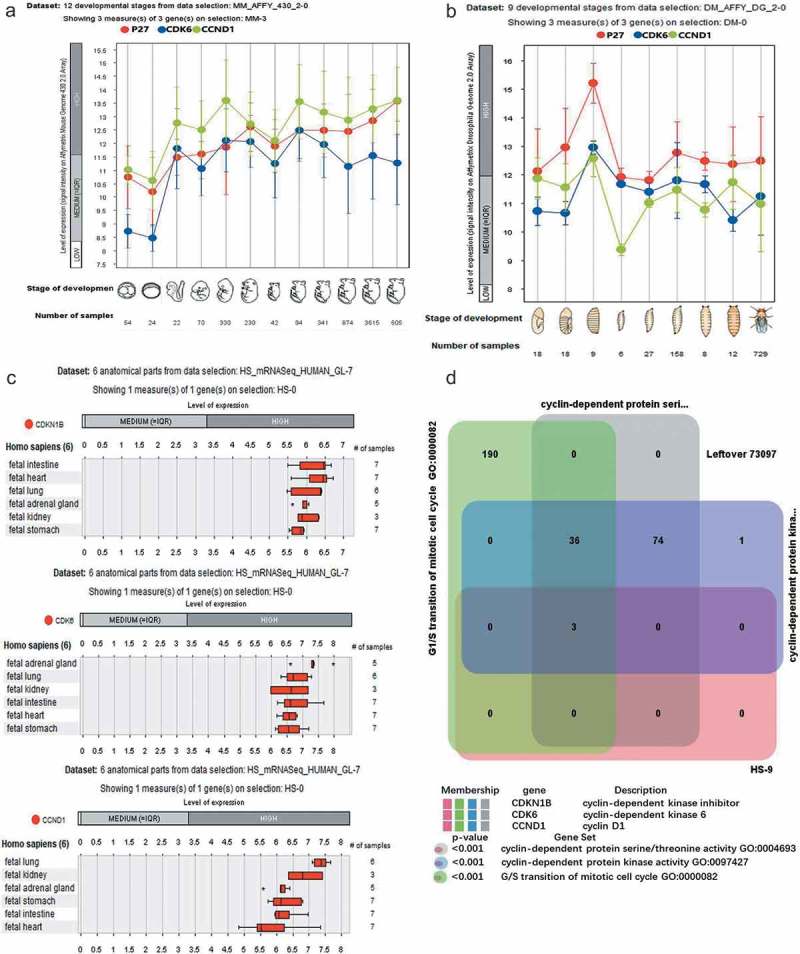
Expression of p27, CDK6, and CCND1 in Drosophila, mice, and humans. (a) Twelve developmental stages from data selections: MM-AFFY-430 −2–0 Showing three measures of P27, CDK6, and CCND1 in mice. The 12 stages were: prenatal_0–1, prenatal_2–4, prenatal_7–8.5, prenatal_9–11, prenatal_11.5–15, prenatal_16-18, postnatal_0, postnatal_1–3, postnatal_4–15, postnatal_16–63, adult_64-255, adult_256-9999. (b) Nine developmental stages from data selections: DM-AFFY-DG −2–0 Showing three measures of P27, CDK6 and CCND1 in Drosophila. The nine stages are: germ band elongation stage embryo, germ band retraction stage embryo, late stage embryo, first instar larval stage, second instar larval stage, third instar larval stage, prepupal development, pupal development, and adult development. (c) Detection of mRNA expression of p27, CDK6, CCND1 in six human organs. The organs included the stomach, lung, heart, kidney, adrenal gland, and intestine. (d) Analysis of p27, CDK6, CCND1 functions in humans. The functions of three genes involved in the regulation including cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine activity, cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity, and G/S transition of mitotic cell cycle.
