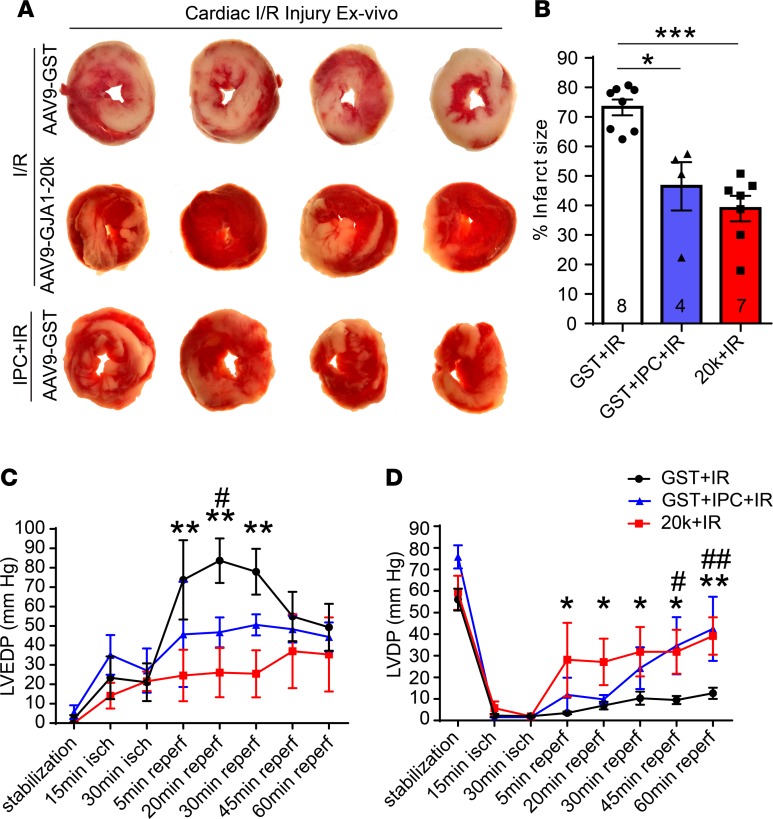
Figure 10. GJA1-20k mimics the IPC protective phenotype seen in heart ex vivo I/R injury.
(A) Representative transverse slices of TTC-stained cardiac sections from Langendorff-perfused hearts isolated from AAV9-GST– or AAV9-GJA1-20k–expressing mice and subjected to ex vivo I/R injury alone (30-minute ischemia and 60-minute reperfusion) or to IPC stimulus prior to the prolonged I/R injury. (B) Infarct size is quantified as a percentage of total slice area, corrected by slice weight (number of hearts quantified per group in shown on the graph). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test. (C) Left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) and (D) left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP) measurements during I/R in Langendorff-perfused hearts isolated from AAV9-GST– or AAV9-GJA1-20k–expressing mice. The hearts were subjected to ex vivo I/R injury alone or to 4 cycles of IPC followed by I/R. GST+IR compared with 20k+IR is indicated by either * or **, and GST+IR compared with GST+IPC+IR is indicated by either # or ##. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ##P < 0.01, 2-way ANOVA. Data are mean ± SEM (GST+I/R, n = 6 hearts; GST+IPC+IR, n = 4 hearts; 20k+IR, n = 5 hearts).