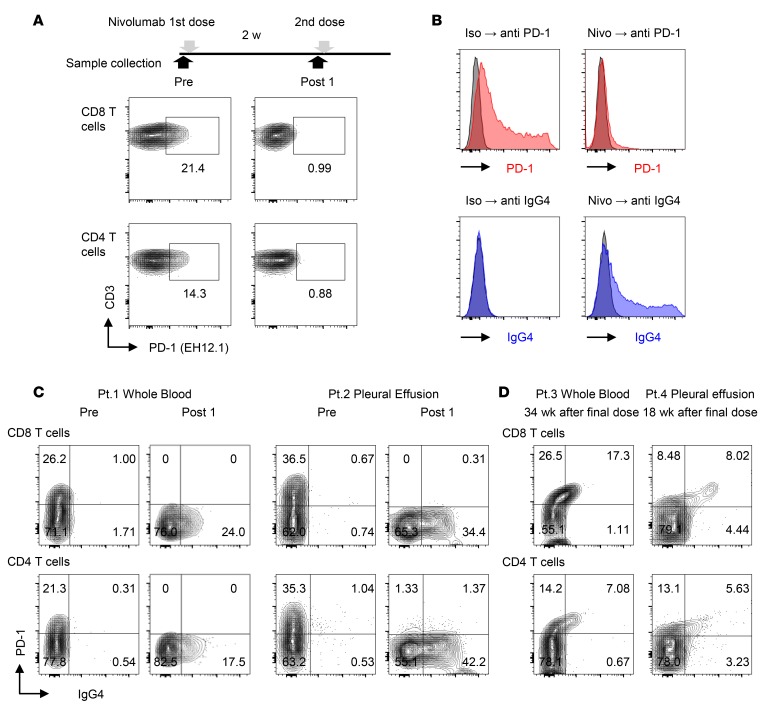
Figure 2. A method for detection of nivolumab binding in T cells of NSCLC patients.
(A) Flow cytometry staining of PD-1 with PD-1 detection antibody (EH12.1) in peripheral blood CD8 and CD4 T cells before injection (Pre) and 2 weeks after the first dose of nivolumab (Post 1). (B) PD-1–transfected HEK293T cells (HEK293T-PD-1) exhibited binding of EH12.1 (left). After treatment with nivolumab, EH12.1 binding was completely abolished, whereas the nivolumab detection antibody (anti-IgG4, HP6025) exhibited the original expression pattern (right). Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (C) Staining of PD-1 by EH12.1 and IgG4 by HP6025 in CD8 and CD4 T cells from fresh whole blood and pleural effusion was evaluated by flow cytometry at pretreatment and 2 weeks after the initial dose of nivolumab. Whole blood from Pt. 1 and pleural effusion from Pt. 2 are shown as representative analyses. (D) Staining of PD-1 (EH12.1) and IgG4 (HP6025) in CD8 and CD4 T cells from fresh whole blood from Pt. 3 and pleural effusion from Pt. 4 were analyzed by flow cytometry at 34 weeks and 18 weeks after the final dose, respectively.