Figure 1.
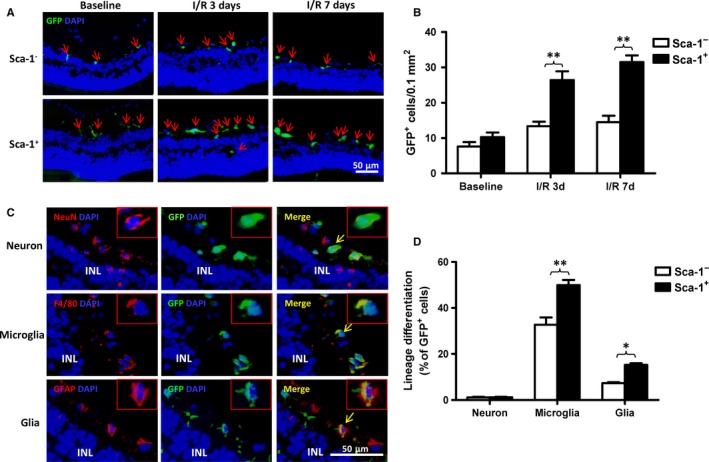
BM‐derived Sca‐1+ cells had greater homing and differentiation capabilities after acute ischaemia‐reperfusion injury. Bone marrow (BM) Sca‐1+ or Sca‐1− cells from young GFP (green fluorescent protein, green, 2 × 106) transgenic mice were used to reconstitute old wild‐type mice, generating Sca‐1+ and Sca‐1− chimaeras, respectively. Acute ischaemia‐reperfusion (I/R) injury was induced 12 weeks later. Progenitor cells in the retina of recipients were evaluated 3 and 7 days post‐I/R injury. Characterisation and quantification by immunolabelling of retinal sections for GFP (A and B) and GFP/NeuN, GFP/F4/80, GFP/GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) double‐positive cells (C and D). BM Sca‐1+ cells had greater capability to home to the retina than Sca‐1− cells (n = 4/group; A and B). There was more cell differentiation into microglia (F4/80) and glia (GFAP) in Sca‐1+ than Sca‐1− chimaeras after retinal injury (C and D; n = 4/group). INL: inner nuclear layer. Data analysis used two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post‐hoc tests for multiple comparisons (B and D). Data shown are mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05
