Figure 2.
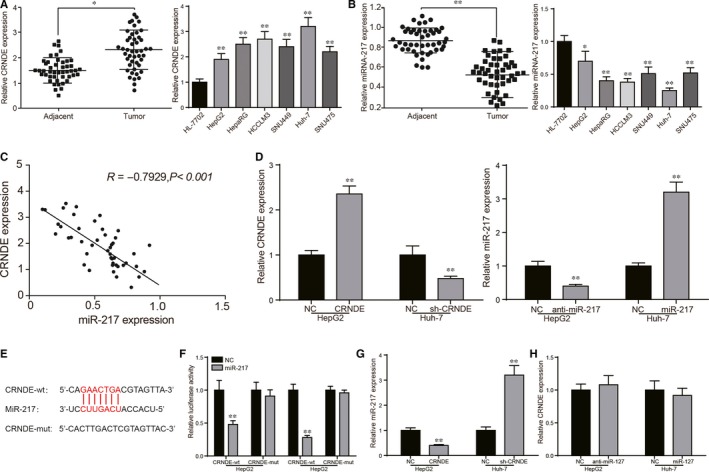
Circumstance of CRNDE/miR‐217 expression in vitro/vivo and the relationship between them. (A) CRNDE expression in tissues and HCC cells. (B) MiR‐217 expression in tissues and HCC cells. (C) Pearson's correlation analysis revealed CRNDE expression was negatively related with miR‐217 expression in HCC tissues. (D) Transfection efficiencies test of CRNDE/sh‐CRNDE and miR‐217/anti‐miR‐217 verified by qRT‐PCR. (E) The sequence of binding sites between CRNDE and miR‐217, and the sequence of mutant CRNDE. (F) Dual luciferase reporter assays showed that miR‐217 could regulate the luciferase activity of CRNDE‐WT, rather than CRNDE‐Mut. (G) QRT‐PCR showed that CRNDE could negatively regulate miR‐217 expression in HCC cells. CRNDE could significantly decrease the expression of miR‐217 in HepG2 cells while sh‐CRNDE could significantly increase the expression of miR‐217 in Huh‐7 cells. (H) MiR‐217 could not inversely regulate CRNDE expression in HCC cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with adjacent/HL‐7702/NC group
