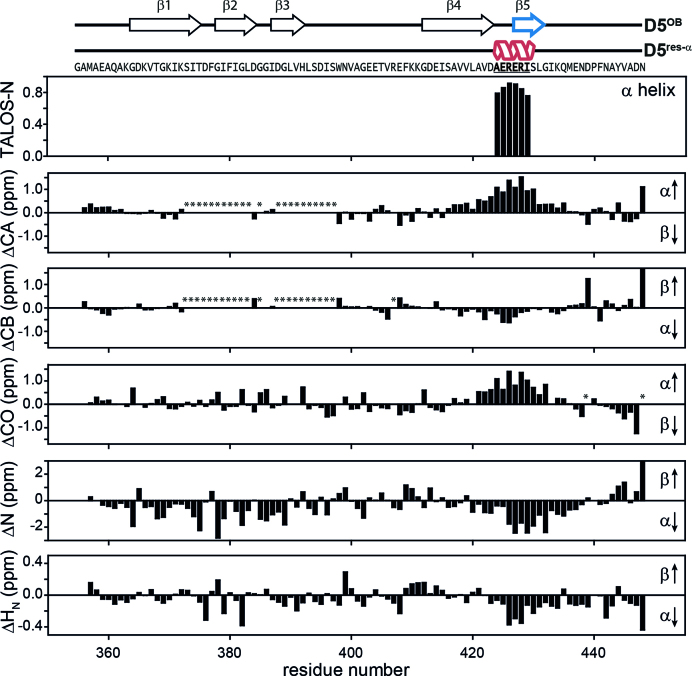
Figure 5.
Structural characteristics of the D5res-α state. The chemical shifts of backbone atoms are sensitive for local structure. Their deviations from random coil values can be used for determination of secondary structure based on experimental data. In the upper plot the fractional secondary structure as calculated from TALOS-N is plotted against the protein sequence (59), where an α-helix is found between A424-I429. The lower plots display 1H, 15N and 13C secondary chemical shifts as a function of residue number. They were calculated as Δ = δobs − δrc (58), where δobs are the observed chemical shifts and δrc are the random coil chemical shifts. δrc were generated using the Javascript provided by Alex Maltsev, on the website of the University of Copenhagen (http://www1.bio.ku.dk/english/research/bms/research/sbinlab/groups/mak/randomcoil/script; 18 April 2018). The expected secondary structure element is indicated within the plot with arrows. All secondary chemical shift values indicate α-helical structure of the sequence stretch A421-G432. The largest values coincide with the AERERI sequence, strongly pointing towards α-helical structure of this particular sequence. In case of ΔCB and ΔN the secondary chemical shifts for N448 are truncated and have a value of 1.9 and 5.7, respectively. Asterisks mark not observed resonances. For clarity primary sequence and secondary structure elements of both rS1-D5 states are displayed on the very top of the figure.