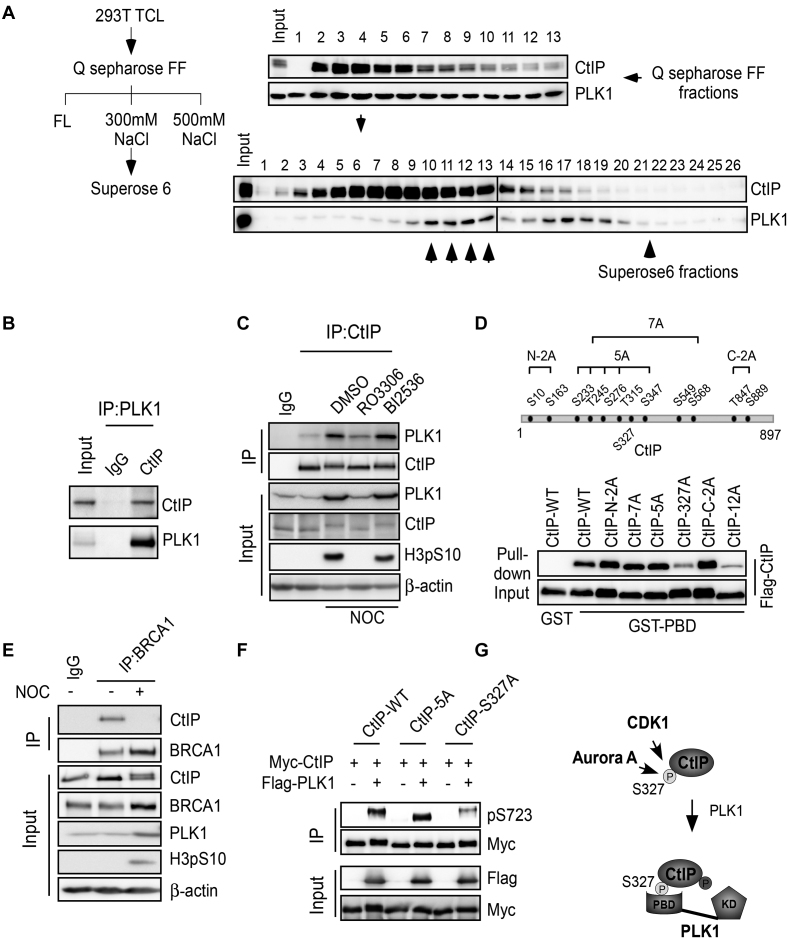
Figure 4.
PLK1 interacts with CtIP in a S327 phosphorylation-dependent manner. (A) Left: Purification scheme. 293T cells were pre-treated with nocodazole for 16 h and lysed. Total cell lysate (TCL) was applied to a pre-equilibrated Q-sepharose FF column. After washing, the bound proteins were eluted with 300 mM NaCl, followed by fractionation on a Superose 6 gel filtration column. Right: Western blotting was performed using the indicated antibodies on alternate fractions to monitor the elution of CtIP and PLK1. Superose 6 fractions (10–13, indicated by the up-arrow) contained both CtIP and PLK1. (B) 293T cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) Unperturbed and nocodazole-arrested 293T cells, pre-treated with or without the indicated drugs, were lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) Top: Twelve putative CDK consensus sites (SP/TP motifs) on CtIP. Bottom: the indicated CtIP constructs were expressed in Sf9 insect cells by baculovirus infection and then used in GST pull-down assays using purified GST-PBD protein as bait. Western blotting was performed to analyze the binding between PBD and CtIP variants. (E) U2OS cells were treated with nocodazole (NOC) for 16 h and then subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) 293T cells were co-transfected with Myc-tagged CtIP variants and Flag-tagged PLK1 expression constructs. Cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (G) The role of S327 phosphorylation in mediating the CtIP binding with PBD and subsequent phosphorylation of CtIP by PLK1. FL, flow through; KD, kinase domain.