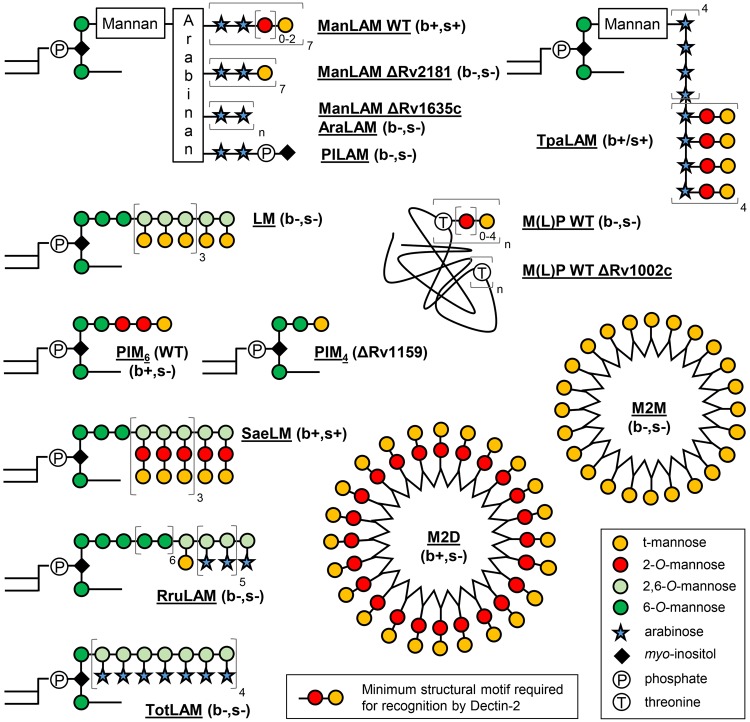
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of the natural and synthetic mannoconjugates evaluated. AraLAM, lipoarabinomannan devoid of caps; LM: lipomannan; ManLAM, mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan; M(L)P, manno(lipo)proteins; M2M, M2D, second-generation mannodendrimers capped with mono- or di-mannosides respectively; PILAM, phospho-myo-inositol-capped lipoarabinomannan; PIM4, phosphatidyl-myo-inositol tetramannosides; PIM6: phosphatidyl-myo-inositol hexamannosides; RruLAM; LAM from R. ruber; SaeLM, LM from S. aerocolonigenes; TotLAM, LAM from T. otitidis; TpaLAM, LAM from Ts. paurometabola. Detailed structures are shown in Fig. S1. (b+/−, s+/−) indicates the ability (+) or not (−) of the mannoconjugates to bind (b) or induce signaling (s) via Dectin-2.