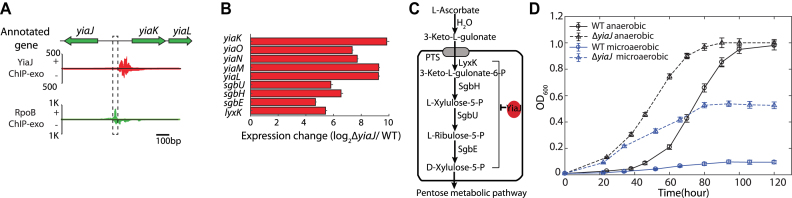
Figure 4.
The regulatory role of the uncharacterized TF YiaJ is involved in the utilization of l-ascorbate in E. coli K-12 MG1655. (A) YiaJ binding sites at the promoter region between yiaJ and the yiaKLMNO-lyxK-sgbH-sgbU-sgbE operon. (B) Expression changes for genes in the yiaJ deletion strain in the yiaKLMNO-lyxK-sgbH-sgbU-sgbE operon compared to the wild type strain. (C) The proposed function of YiaJ is to repress the ascorbate utilization pathway, therefore regulating the level of d-xylulose-5-P that feeds into the pentose phosphate pathway. (D) Growth curve of wild type and yiaJ deletion strains at ascorbate as the carbon source under anaerobic and microaerobic conditions, respectively.