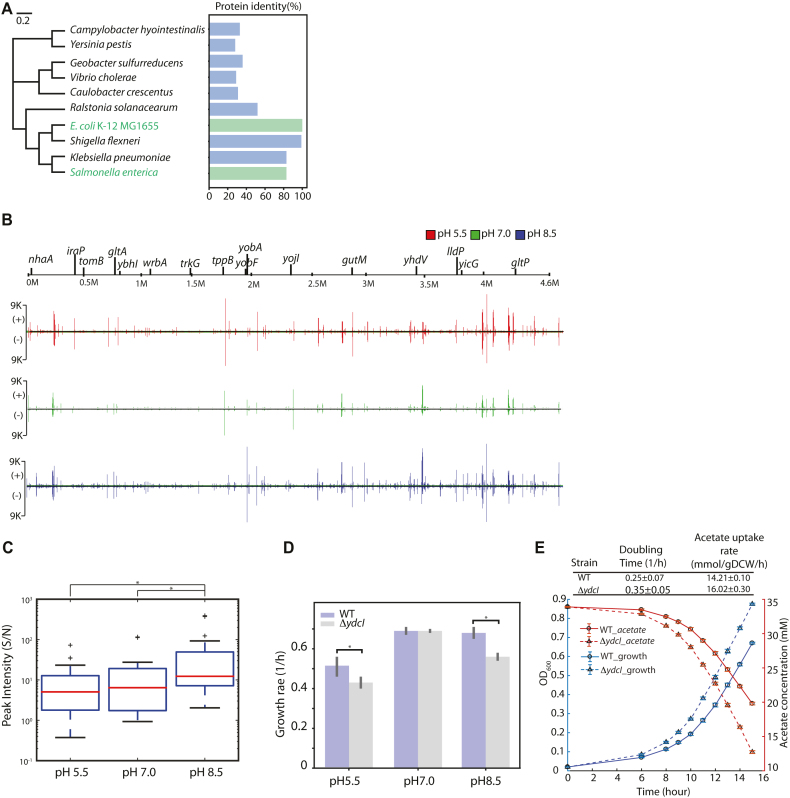
Figure 5.
The regulatory role of the uncharacterized TF YdcI is involved in proton and acetate metabolism in E. coli K-12 MG1655. (A) Phylogenetic trees displaying the relatedness of YdcI from E. coli K-12 MG1655 and from Salmonella enterica. (B) Genome-wide YdcI DNA binding. YdcI binding across the genome was compared under different pH conditions in E. coli K-12 MG1655 by ChIP-exo. (C) Peak intensity (Signal/Noise) of YdcI ChIP-exo binding sites at pH 5.5, pH 7.0, and pH 8.5. Among the three different pH conditions, peak intensity was most active at pH 8.5 (* indicates rank sum test P-value < 0.05). (D) The growth rate of wild type and ydcI deletion strain at low pH, neutral pH, and high pH media. (E) Growth and acetate uptake rates of wild type and ydcI deletion strains in acetate growth medium.