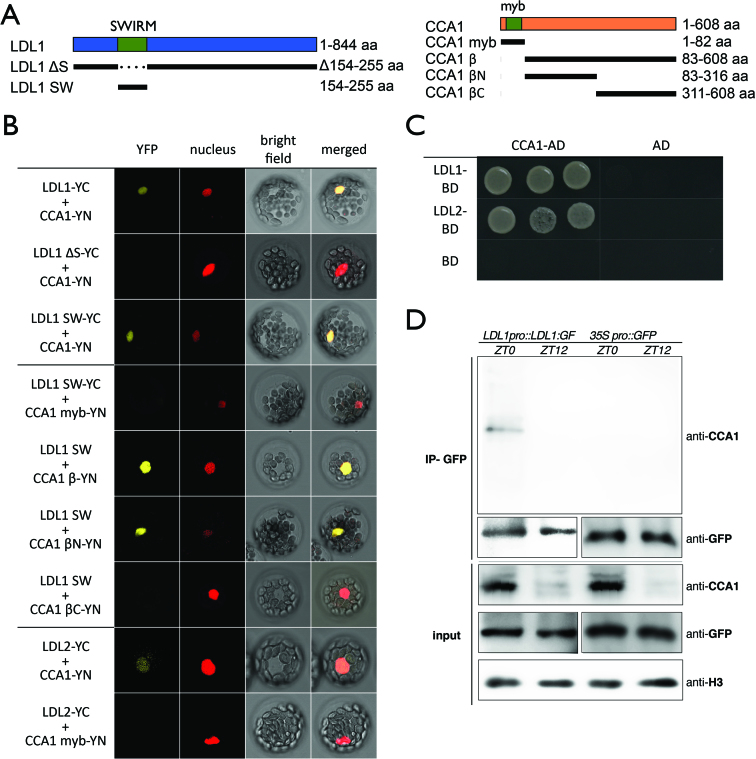
Figure 1.
LDL1 and LDL2 interacts with CCA1. (A) Schematic representation of deletions in LDL1 and CCA1 constructs. LDL1ΔS: deletion of 154–255aa; LDL1SW: 154–255aa; CCA1myb: 1–82aa; CCA1β: 83–608aa; CCA1βN: 83–316aa; CCA1βC: 311–608aa. SWIRM: SWIRM domain of LDL1; myb: myb-domain of CCA1. (B) BiFC assays in Arabidopsis protoplasts showing interaction of LDL1/LDL2 with CCA1 in living cells. Different regions of LDL1 and CCA1, and full-length of LDL2 were fused with the N terminus (YN) or C terminus (YC) of YFP and co-delivered into Arabidopsis protoplasts. The nucleus was indicated by mCherry carrying a nuclear localization signal. (C) Yeast two hybrid analysis of the interaction of LDL1/LDL2 with CCA1. LDL1-BD/LDL2-BD with CCA1-AD was co-transformed into the yeast strain AH109. The transformants were plated on the SD/-Leu-Trp-His medium. (D) Co-IP of LDL1:GFP with CCA1 in LDL1pro::LDL1:GFP transformed Arabidopsis. Western blot (WB) was performed with the indicated antibodies.