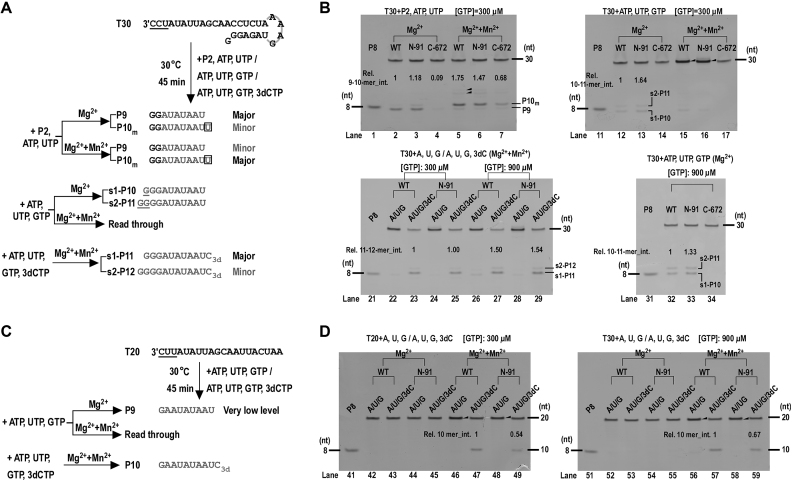
Figure 7.
Mn2+ and the starting template sequence affected the overall synthesis activities of NS5B and the effect brought by NTD deletion. (A) Reaction flow-charts and product designations of the P2-based assays and the de novo (P2-free) assays both using T30 as the template. (B) Assessment of the impact on the NS5B synthesis by Mn2+ and the NTD deletion. In the P2-based assays the primary product was a 10-mer mismatch product (P10m) instead of the 9-mer correct product (P9) when ATP and UTP were supplied and 1 mM Mn2+ was supplemented. Longer products (solid triangle in the top left gel) likely derived from Mn2+-induced misincorporation were also evident. The WT and N-91 read through the template T30 (indicated by band intensity enhancement at the migration position of the template and the solid triangle in the top right gel) in the de novo assays when ATP, UTP and GTP were supplied and 1 mM Mn2+ was supplemented. (C) The reaction flow-chart and product designations of the de novo assays using a 20-nt template (T20) with a different starting template sequence from the T30. (D) Assessment of the WT and N-91 synthesis using the T20-based assays. The WT and N-91 had very low activities under Mn2+-free condition if compared to data of the T30-based assays. When 1 mM Mn2+ was supplemented, both the WT and N-91 read through (indicated by the solid triangles) the template T20 with ATP, UTP and GTP supplied. The reactions with ATP, UTP, GTP and 3′-deoxy-CTP (3dCTP) supplied were designed to largely inhibit the read-through activity and to allow a comparison of the synthesis levels of the WT and N-91 in the presence of Mn2+. In panels A and C, the starting trinucleotides of the T30 and T20 RNA are underlined for comparison.