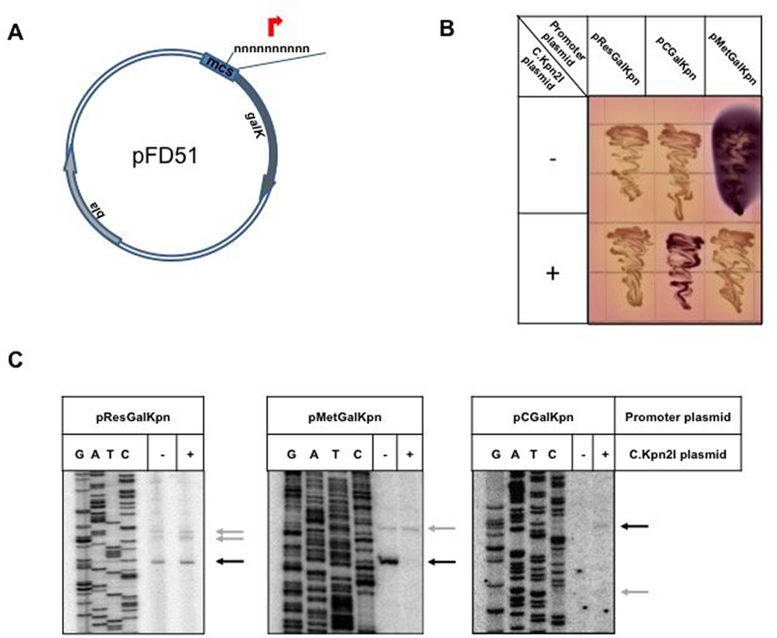
Figure 2.
In vivo mapping of Kpn2I promoters. (A) The pFD51 promoter-trap plasmid with its multiple cloning site (mcs) used to clone DNA fragments in front of promoterless galK gene is schematically shown. (B) Overnight growth of E. coli cells harboring pFD51-based plasmids with Kpn2I promoters cloned upstream of galK on a McConkey agar plate. Cells in some cultures also contained a compatible plasmid producing C.Kpn2I. Colonies formed by cells carrying empty vector pFD51 are of the same (white) color as colonies of cells carrying pCGalKpn (not shown). (C) RNA was purified from E. coli cell cultures whose growth is shown in B and subjected to primer extension reaction with a galK-specific primer. Primer extension end points are marked with horizontal arrows and correspond to transcription start points shown in Figure 1.