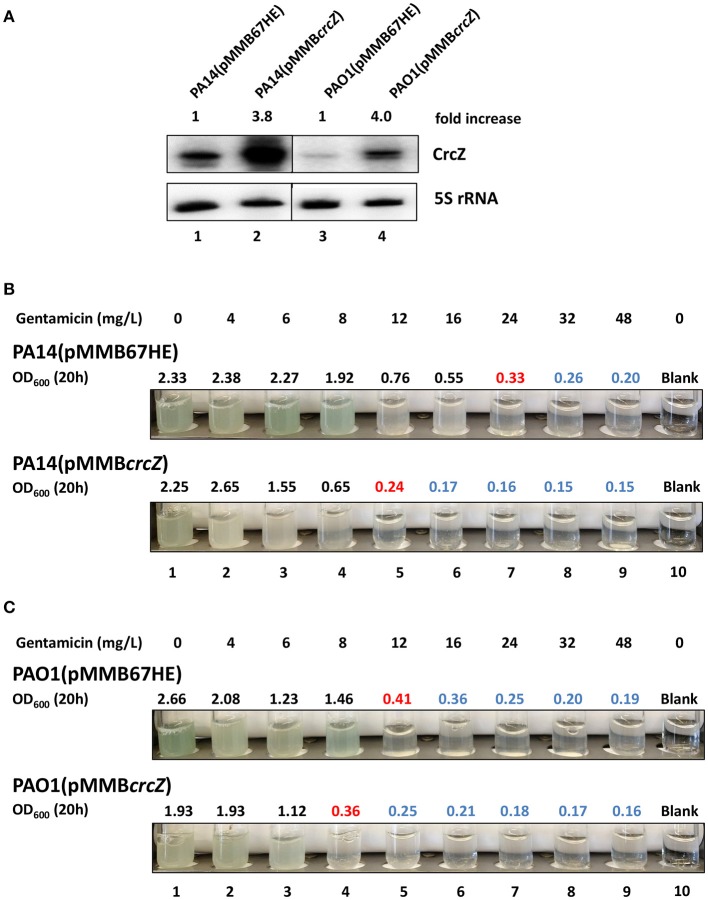
Figure 4.
Over-production of CrcZ results in increased susceptibility to gentamicin. (A) PA14 and PAO1 harboring plasmid pMMB67HE and plasmid pMMBcrcZ, respectively, were grown in SCFM for 20 h. The cells were harvested and the CrcZ levels were determined by Northern-blot analysis. 5S rRNA served as a loading control. The fold increase was calculated by dividing the signal intensity of CrcZ by the corresponding signal of 5S rRNA and normalized to the signal obtained with the respective wild type strain harboring plasmid pMMB67HE that was set to 100%. Lanes 1 and 2 contain RNA extracted from strains PA14 (pMMB67HE) and PA14 (pMMBcrcZ), respectively. Lanes 3 and 4 contain RNA extracted from strains PAO1(pMMB67HE) and PAO1(pMMBcrcZ), respectively. (B,C) MIC determination for gentamicin of PA14 (B) and PAO1 strains (C). The cells harboring plasmid pMMB67HE (upper panels) and plasmid pMMBcrcZ (lower panels), respectively, were grown as described above. The different concentrations of gentamicin added are indicated on top. Pictures were taken and the OD600 was measured 20 h after inoculation. The antibiotic concentrations in the presence of which the cells did not grow above OD600 of 0.5 (marked in red) were considered as MIC. All OD600 values above this gentamicin concentration are depicted in blue indicating toxicity. The experiments were performed in duplicate, revealing the same MICs. Only one representative experiment is shown.