Fig. 1.
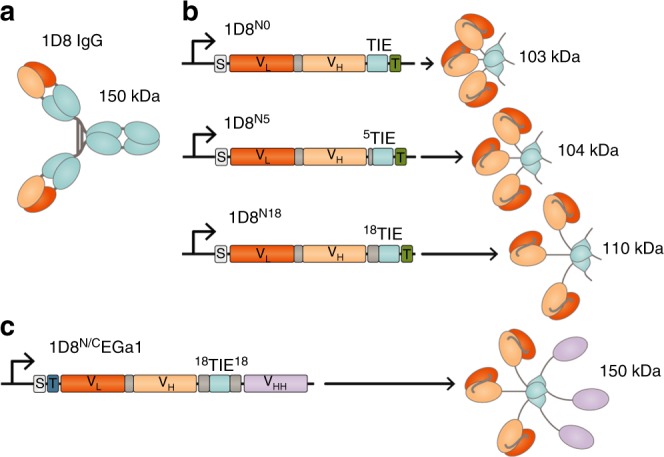
Schematic diagrams of 4-1BB-agonistic trimerbodies. Protein structure of the anti-4-1BB IgG (a) and the gene layout (left) and protein structure (right) of monospecific (b) and bispecific trimerbodies (c). The variable regions derived from 1D8 antibody are represented in orange, the anti-EGFR VHH EGa1 in violet, the structural domains in light blue, and the linker regions in gray. The 1D8 scFv-based N-terminal trimerbodies’ (1D8N) gene constructs (b) contain a signal peptide from oncostatin M (white box) and the 1D8 scFv gene (VL-VH) connected directly or through flexible linkers to the mouse TIEXVIII domain. In the bispecific 1D8N/CEGa1 trimerbody (c), the anti-human EGFR VHH EGa1 is fused to the C-terminus of 1D8N18 through a flexible linker. Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. His6-myc tag (green box) and FLAG-strep tags (dark blue box) were appended for immunodetection
