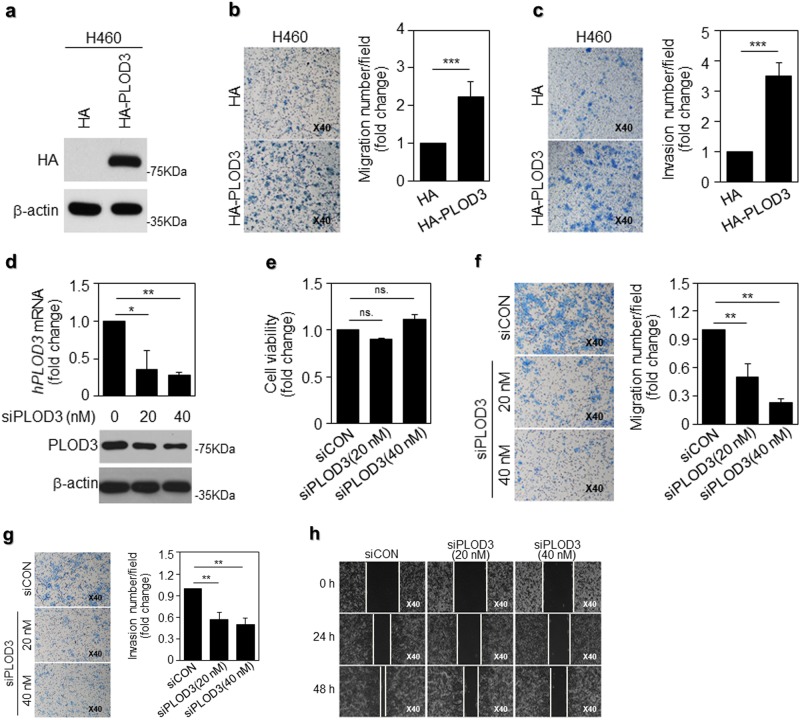
Fig. 2. PLOD3 possesses greater potential to promote lung cancer malignancy.
a PLOD3 protein expression was assessed via western blot analysis, following transfection of HA-PLOD3 in H460 cells for 48 h. b A transwell assay was performed to evaluate the motility of PLOD3-overexpressing H460 cells. PLOD3 displayed superior potential to promote cell migration. The relative numbers of migratory cells were determined and presented as the mean ± SD values from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test. ***P < 0.001. c The invasion assay revealed different cell motilities in PLOD3-overexpressing lung cancer cells. PLOD3 expression promoted the invasion of H460 cells. The relative numbers of invasive cells were determined and presented as the mean ± SD values from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test. ***P < 0.001. d PLOD3 protein and mRNA levels were determined via western blotting (lower) and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR; upper), respectively, after the indicated concentration of siPLOD3 was transfected in R-H460 cells for 24 h. The qRT-PCR data are expressed as the mean ± SD values *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. e The cell viability assay for siPLOD3-treated cells for 24 h; x-axis: siCON, siPLOD3 (concentration). f A transwell assay was conducted to evaluate the motility of PLOD3 knockdown R-H460 cells at 12 h. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test. **P < 0.01. g Cell invasion assay revealed that siPLOD3 had a limited effect on pro-metastasis at 24 h in R-H460 cells. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test. **P < 0.01. h R-H460 cells were treated with siPLOD3 and then incubated for 24 and 48 h. The cells were then scraped with a sterile 200-μl pipette tip for the scratch assay