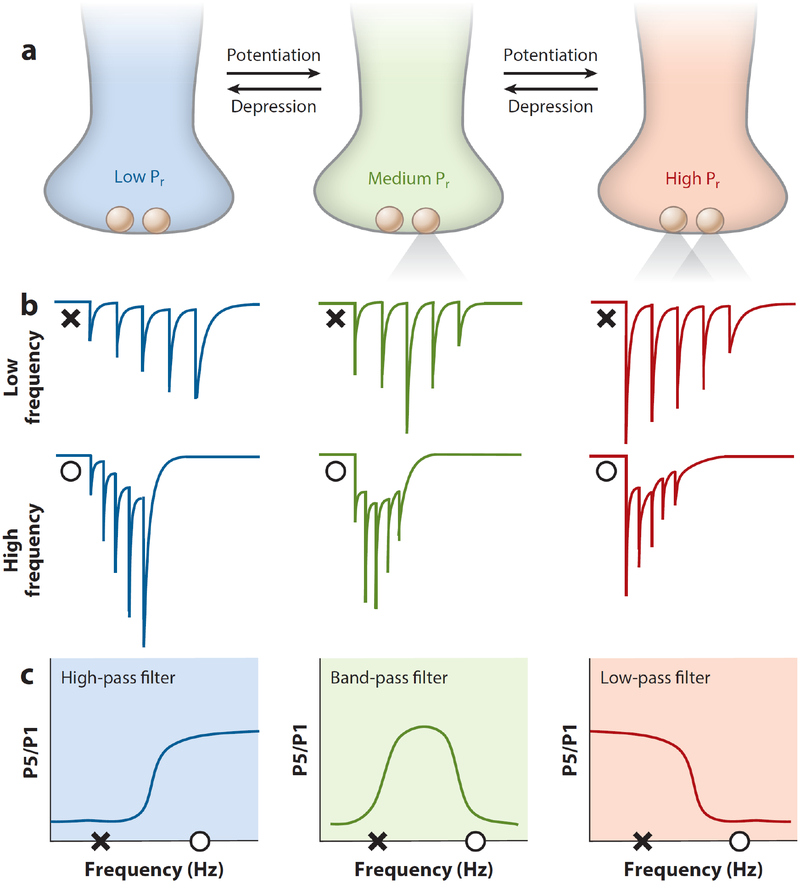
Figure 3.
Long-term presynaptic plasticity modifies short-term plasticity and synaptic filtering. (a) PreLTP and preLTD can shift Pr of individual terminals between low, medium, and high modes. (b) Schematic EPSCs resulting from five input pulses at relatively low and high frequencies across each Pr. (c) Schematic depicting synaptic filtering of excitation across each Pr. Low-, medium-, and high-Pr synapses can respectively exhibit high-pass, band-pass, and low-pass filtering. The amplitude ratio of P5 to P1 as a function of input frequency is shown. X indicates low frequency. O indicates high frequency. Long-term presynaptic plasticity can shift the range and type of filtering at a given synapse. Abbreviations: EPSC, excitatory postsynaptic current; P5/P1, pulse 5/pulse 1; Pr, release probability; preLTD, presynaptic long-term depression; preLTP, presynaptic long-term potentiation.