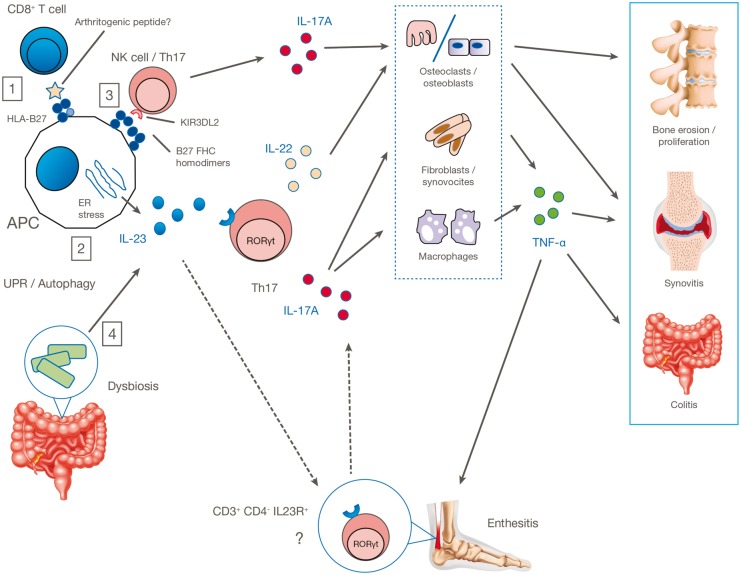
Fig. 1.
Proposed pathogenic mechanisms in AS
(1) Autoreactive CD8+ T cells may recognize the arthritogenic peptides displayed by HLA-B27 on the APC surface; (2) HLA-B27 misfolding in APCs leads to ER stress and consequent overproduction of IL-23; (3) abnormal cell-surface expression of HLA-B27 leads to interaction with innate immune receptors such as KIR3DL2 on CD4+ T cells and promotes type 17 immune responses; (4) HLA-B27 causes intestinal dysbiosis, resulting in overexpression of the IL-17A/IL-23 axis with activation of Th17 or other CD4+ cells, γδ T cells, mast cells, neutrophils and other innate immune cells. This leads to production of IL-17A, IL-22, TNF-α, IFN-γ and other cytokines that target organs and tissues directly or through tissue-resident effector cells. APC, antigen-presenting cell; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; IL23R, IL-23 receptor; KIR3DL2, killer immunoglobulin-like receptor; UPR, unfolded protein response.