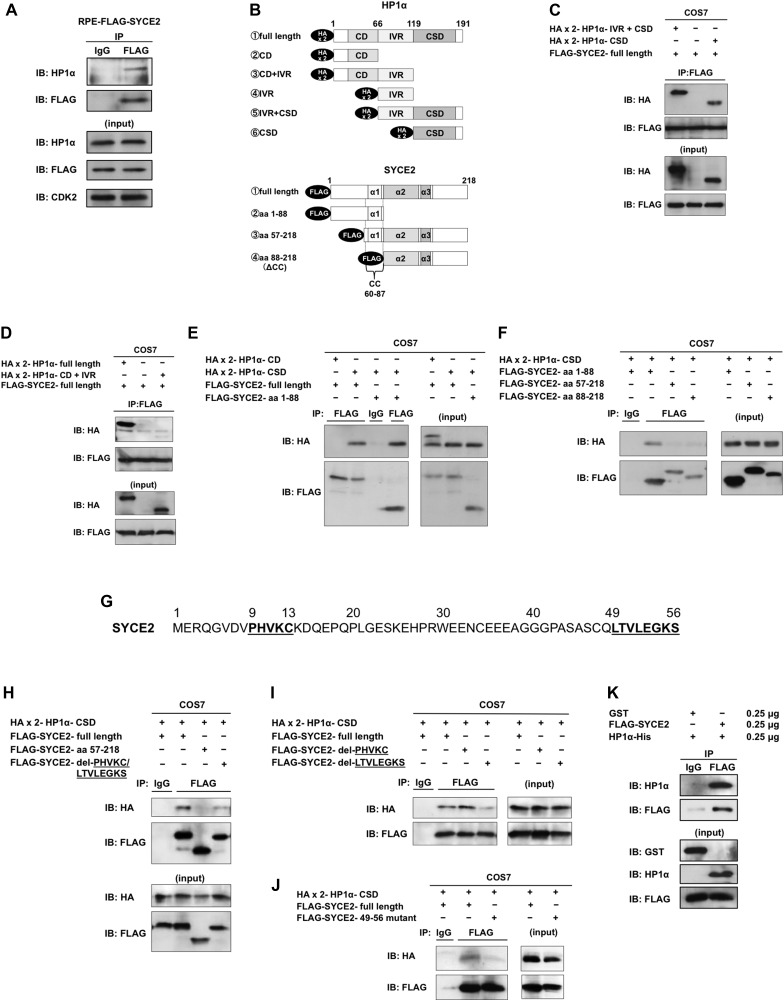
Figure 5. SYCE2 directly binds to the chromoshadow domain of HP1α.
(A) Interaction of FLAG-SYCE2 with HP1α in FLAG-SYCE2-expressing RPE cells. 500 μg of total cell lysates was immunoprecipitated using the anti-FLAG antibody produced in mouse or normal mouse IgG as a negative control and visualized by Western blotting using the anti-HP1α antibody produced in goat as a primary antibody and an HRP-linked anti-goat IgG antibody produced in rabbit as a secondary antibody. (B) Schematic diagrams of the HA-tagged deletion mutants of HP1α and the FLAG-tagged SYCE2. (C–F, H–J) Analyses of interactions between each deletion mutant (C–F, H, I) or the mutant causing amino acid substitutions (J) of SYCE2 tagged with FLAG and that of HP1α tagged with HA. The “FLAG-SYCE2-49-56 mutant” in (J) has point mutations resulting in the substitution of the hydrophobic LTVLEGKS sequence in the amino acids 49–56 of SYCE2 into a non-hydrophobic ETDEEENS sequence. Expression vectors for the indicated mutants of SYCE2 and HP1α were transiently co-transfected into COS7 cells. 500 μg of total cell lysates of these cells was immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG antibody or normal IgG and then analyzed by immunoblotting with the anti-HA antibody or the anti-FLAG antibody. 30 μg of the input was also analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody. (G) Sequence of the N-terminal region (amino acids 1–56) of the SYCE2 protein. The PHVKC sequence similar to the canonical PXVXL motif and the hydrophobic sequence LTVLEGKS are underlined. (K) Pull-down assay using the indicated amounts of recombinant proteins for FLAG-tagged full-length SYCE2 in the presence of GST as a negative control experiment (left lane) and full-length HP1α (right lane). CD, chromodomain; IVR, intervening region; CSD, chromoshadow domain; α1-3, α-helical structures; CC, coiled-coil domain.