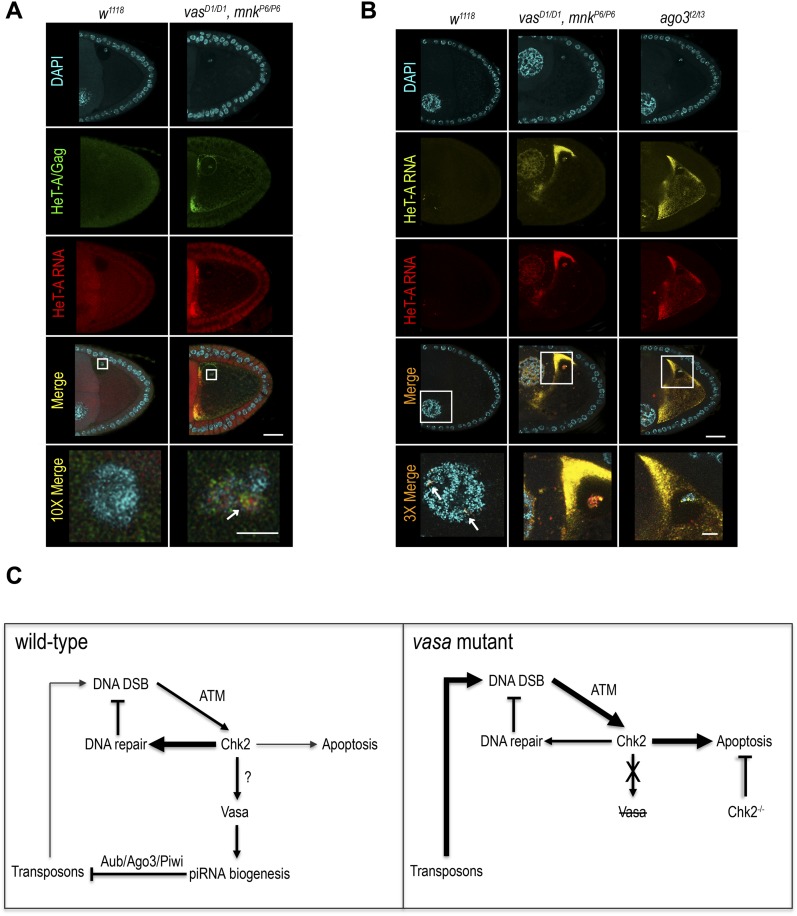
Figure 5. Vasa couples the DNA damage response machinery and the piRNA pathway in Drosophila female germline.
(A) In situ detection of HeT-A mRNA by FISH and immunohistochemical detection of HeT-A/Gag protein in WT (w1118) and vasD1/D1, mnkP6/P6 double mutant ovaries. Arrow indicates co-localization of HeT-A mRNA and HeT-A/Gag protein signals. Scale bars indicate 20 and 5 μm (10× magnification). (B) In situ detection of HeT-A mRNA by FISH in WT (w1118), vasD1/D1, mnkP6/P6 double mutant, and agot2/t3 single mutant ovaries. Arrows indicate sites of HeT-A mRNA transcription. Scale bars indicate 20 and 5 μm (3× magnification). (C) In WT flies, the occurrence of DNA DSBs activates Chk2 kinase that regulates several mechanisms that together antagonize deleterious effects of DNA damage. Chk2 might directly or indirectly target Vasa that in turn affects piRNA biogenesis and transposon control, reducing the transposon-induced DSBs. Accordingly, DNA damage induced by high levels of transposons in vas mutants triggers DNA damage–induced apoptosis resulting in oogenesis arrest. Oogenesis can be restored by depletion of Chk2; however, transposon deregulation persists and causes severe nuclear damage and embryogenesis arrest preventing distribution of transposon-induced, detrimental mutations within the population.