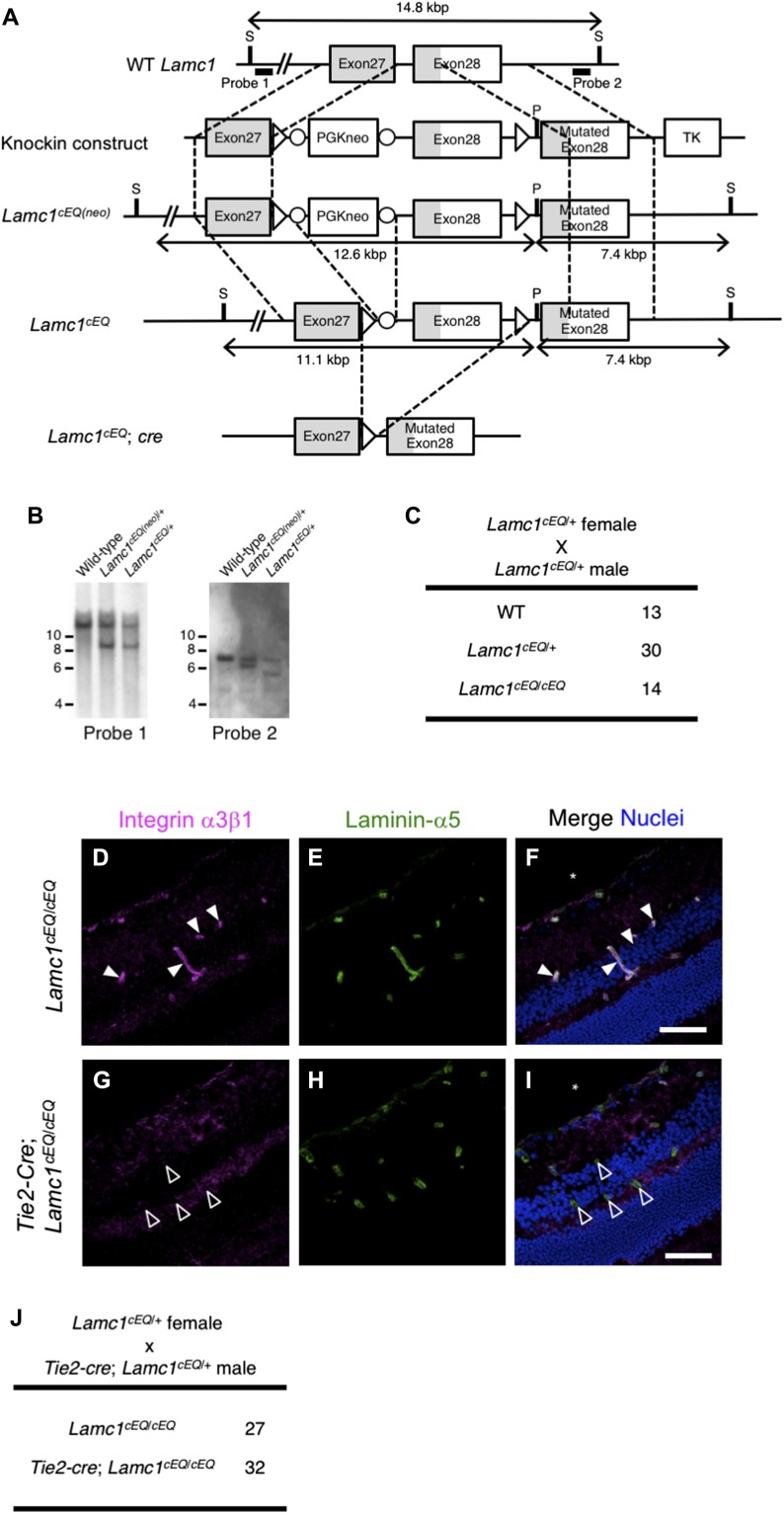
Figure 4. Generation of γ1 EQ conditional knock-in mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the generation of Lamc1cEQ. The open boxes represent exons. The protein coding sequences are indicated in gray. The targeting construct was designed to replace WT exon 28 encoding Glu at residue 1,605 with a floxed exon 28 followed by a mutated exon 28 encoding Gln at residue 1,605. The probes used for Southern blotting are indicated by bold lines. (B) Southern blot analyses of genomic DNA from WT, Lamc1cEQ(neo)/+, and Lamc1cEQ/+ offspring after digestion with SexAI and PacI. The detection of 9.0 and 7.4 kbp fragments with probe 1 and probe 2, respectively, in the Lamc1cEQ(neo)/+ lanes indicates occurrence of the expected homologous recombination. The detection of a 7.4 kbp fragment with probe 1 in the Lamc1cEQ/+ lane indicates that the neomycin-resistance gene has been removed from the Lamc1cEQ(neo) allele by the Cre-loxP system. (C) Genotypes of offspring obtained from Lamc1cEQ/+ intercrosses. (D–I) Histochemical analyses of Lamc1cEQ/cEQ (D–F) and Tie2-cre;Lamc1cEQ/cEQ (G–I) retinas. (D, G) In situ binding of recombinant integrin α3β1 (magenta) to frozen retinal sections. (E, H) Counterstaining of vascular BM with an anti–laminin-α5 antibody (green). Merged images with nuclear staining (blue) are also shown (F and I). Retinal vasculatures are indicated by filled (Lamc1cEQ/cEQ) and open (Tie2-cre;Lamc1cEQ/cEQ) arrowheads. Bars, 50 μm. (J) Genotypes of offspring obtained from mating between Lamc1cEQ/+ female and Tie2-cre;Lamc1cEQ/+ male mice. Only Lamc1cEQ/cEQ and Tie2-cre;Lamc1cEQ/cEQ mice are shown. S, SexAI restriction site; P, PacI restriction site; TK, thymidine kinase gene.