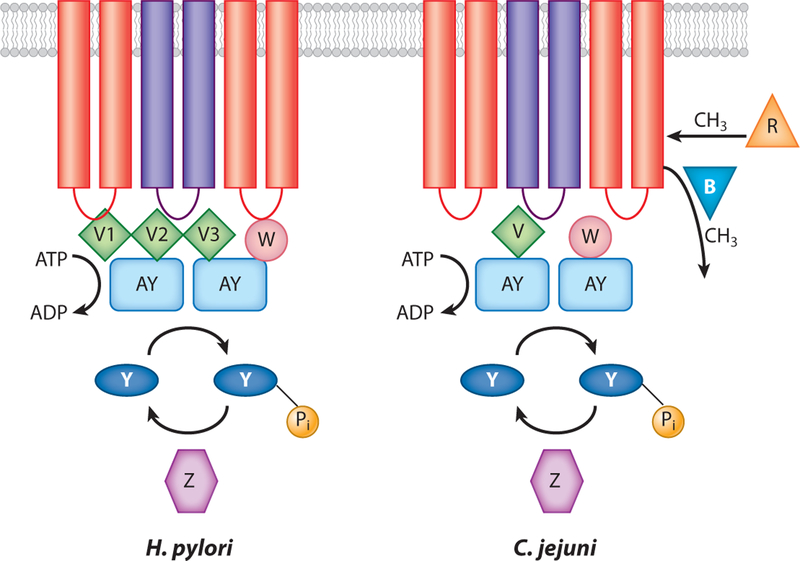
Figure 3.
Chemotaxis signal transduction systems of Campylobacter jejuni and Helicobacter pylori. Transmembrane chemoreceptors are shown as purple and red bars interacting with the coupling proteins CheW (W) or CheV (V). H. pylori contains three CheV proteins, termed CheV1 (V1), CheV2 (V2), and CheV3 (V3). The coupling proteins in turn interact with CheA, also called CheAY (AY), which catalyzes a kinase reaction using ATP as the phosphodonor. The phosphoryl group is passed to CheY (Y) and removed by CheZ (Z). C. jejuni contains CheR (R) and CheB (B), which methylate and demethylate, respectively, the chemoreceptors in other microbes. H. pylori and C. jejuni also contain cytoplasmic chemoreceptors that are not shown but are presumed to participate in the same protein-protein interactions.