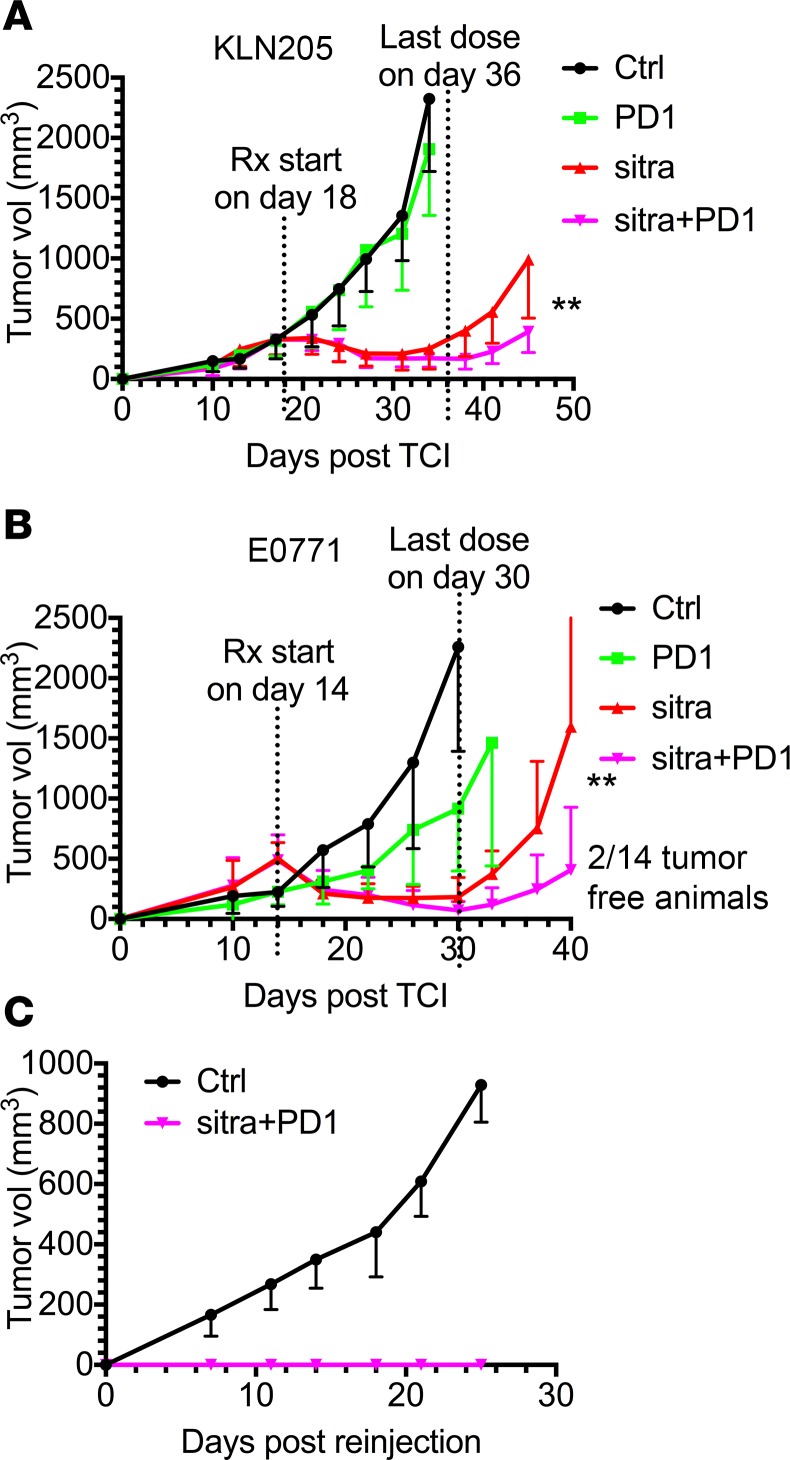
Figure 6. Sitravatinib enhances the efficacy of PD-1 blockade.
(A and B) In vivo assessment of treatment response of subcutaneously or orthotopically implanted tumors (n = 12–14/group) in combination with PD-1 blockade. We injected 0.5 × 106 KLN205 cells (A) subcutaneously into 6-week-old DBA/2 mice, and 0.5 × 106 E0771 cells (B) were injected orthotopically into the mammary fat pads of 6-week-old female C57BL/6 mice. Therapy was initiated in mice with a tumor volume of 300 mm3 (KLN205) or 500 mm3 (E0771) and included control (Ctrl, vehicle, once per day), anti–PD-1 (PD-1, i.p. 10 mg/kg, every 3 days), sitravatinib (sitra, p.o. 20 mg/kg, once per day), or anti–PD-1 in combination with sitravatinib at the indicated dose. Mice were treated for 2.5 weeks. **P < 0.01 anti–PD-1 in combination with sitravatinib vs. sitravatinib alone by t test. Two of fourteen mice bearing E0771 tumors treated with the combination therapy showed complete remission and stayed tumor free for 50 days. (C) Rechallenge growth curve of the 2 tumor-free animals from B. We injected 0.5 × 106 E0771 cells orthotopically into the mammary fat pads of 6-week-old female C57BL/6 mice (Ctrl, n = 4) and on the contralateral side from the original injection of the 2 tumor-free animals.