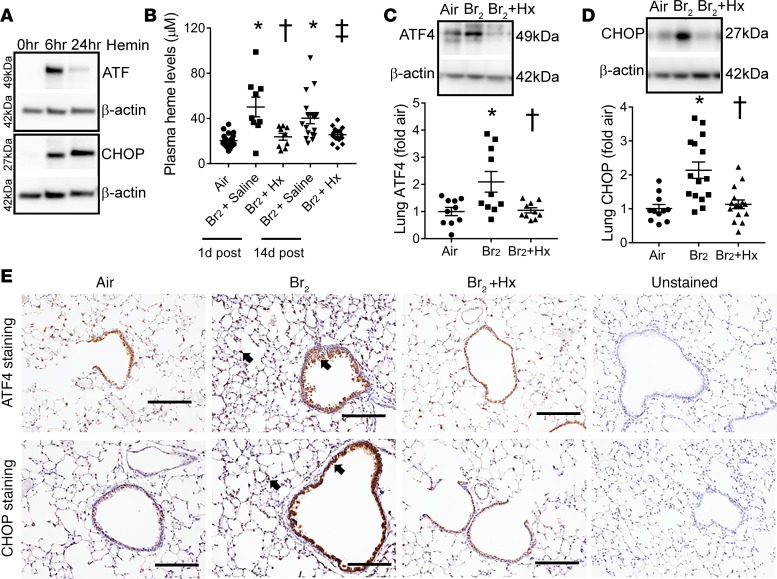
Figure 8. Heme scavenging attenuates ER stress.
Immunoblot analysis showed that the incubation of the human bronchial epithelial cells with hemin (a form of heme, 25 μM), increased the ER stress markers ATF4 and CHOP (n = 3) (A) at 6 and 24 hours after hemin challenge. In addition, male C57BL/6 mice were exposed to air or Br2 gas (400 ppm, 30 minutes) and then returned to room air. Some Br2-exposed mice were given an intraperitoneal injection of purified human hemopexin (Hx) (4 μg/g BW) 1 hour after Br2 exposure. All air-exposed mice and some Br2-exposed mice received saline injection as an appropriate control. Hx attenuated plasma total heme levels in Br2-exposed mice (n = 9–24) (B). Immunoblotting showed that Hx lowered Br2-induced ER stress markers, ATF4 (n = 10) (C) and CHOP (n = 11–15) (D), in mouse lungs 14 days after Br2 exposure. Similarly, immunohistochemical staining of lung sections showed an increased accumulation of ATF4 and CHOP (n = 4–5) (E) (arrows showing brown stain) lining bronchioles and in the lung parenchyma in Br2-exposed mice 14 days after exposure. Hx lowered ATF4 and CHOP levels. Values are mean ± SEM. All animals were males. Scale bars are 200 µm. For A, *P < 0.05 versus air + saline, †P < 0.05 versus Br2 + saline (1 day after), and ‡P < 0.05 versus Br2 + saline (14 days after); for B and C, †P < 0.05 versus Br2 + saline (14 days after) by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.