Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Microbial signals are required for PMP in Tet2−/− mice.
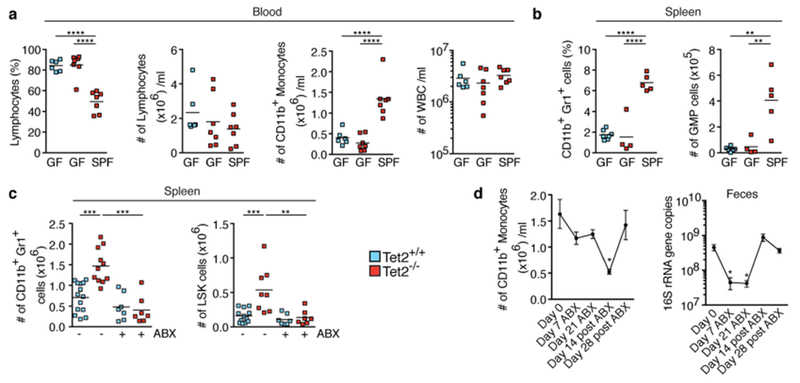
a, b, Germ-free, SPF-housed Tet2−/− mice that are over 40 weeks old, and germ-free wild-type controls, analysed for percentage of lymphocytes (a left), numbers of lymphocytes (a middle left), numbers of CD11b+ monocytes (a middle right) and numbers of leukocytes (WBC) (a right) (n = 6 (Tet2+/+, GF), 7 (Tet2−/−, GF) or 7 (Tet2−/−, SPF) mice), and percentage of CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells (b left) and numbers of GMP cells (b right), (n = 7 (Tet2+/+, GF), 4 (Tet2−/−, GF) or 5 (Tet2−/−, SPF) mice). c, Mice treated with antibiotics (ABX) before onset of PMP (see schematic in Fig. 3c. Numbers of CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells (left; n = 14 (Tet2+/+, no ABX), 11 (Tet2−/− no ABX), 7 (Tet2+/+, with ABX) or 7 (Tet2−/−, with ABX) mice) and LSK cells (right; n = 12 (Tet2+/+, no ABX), 8 (Tet2−/−, no ABX), 7 (Tet2+/+, with ABX) or 7 (Tet2−/−, with ABX) mice). d, Tet2−/− mice monitored for the number of CD11b+ monocytes (left, n = 7 mice) and 16S gene copies in the faeces (right, n = 6 mice) before, during and after antibiotics treatment. Mean ± s.e.m., repeated measures one-way ANOVA, Sidak’s post hoc test. In a–c, centre is mean, one-way ANOVA, Sidak’s post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.
